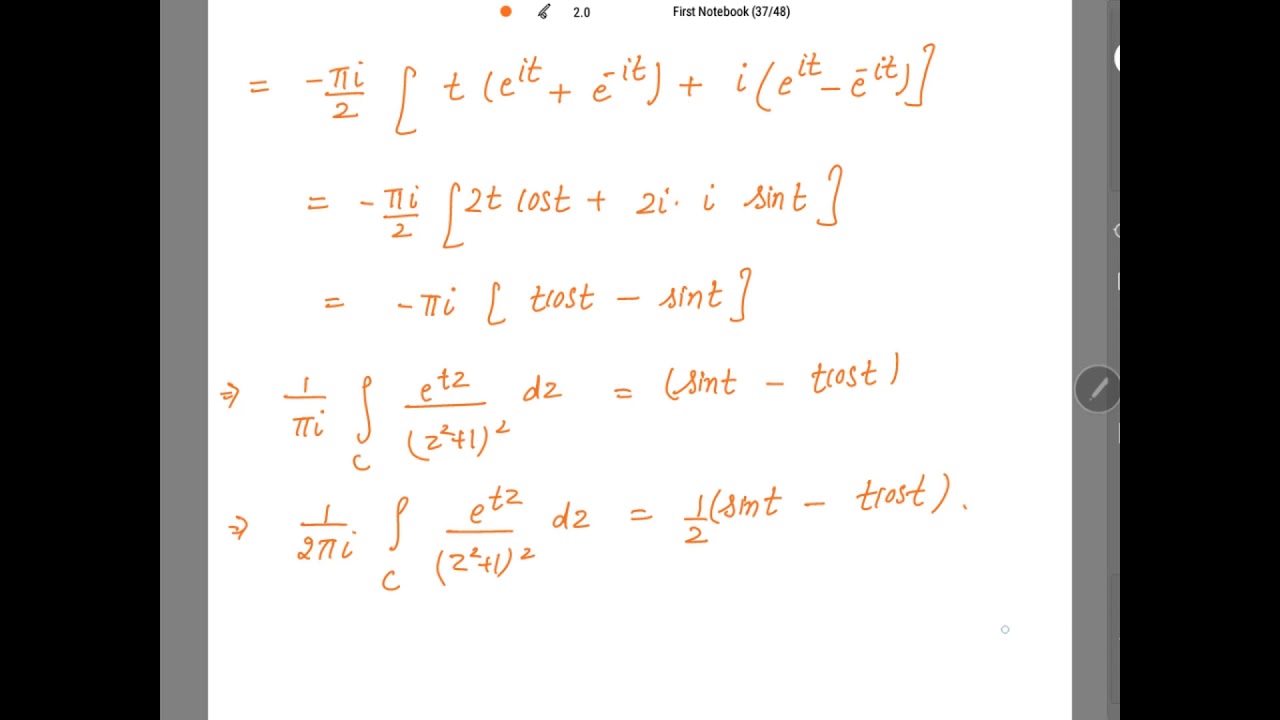
Lesson 3 Solved examples of Cauchy's integral Formula YouTube
Theorem 6: Medium Value theorem of Gauss. In the same conditions as Cauchy's integral formula, it is fulfilled. f(a)= 1 2π ∫2π 0 f(a+reiθ)dθ f ( a) = 1 2 π ∫ 0 2 π f ( a + r e i θ) d θ. The proof of this fact is easy, it is enough to observe that in the Cauchy's integral formula we parametrize C.

complex analysis How to apply cauchy integral formula. Mathematics Stack Exchange
4 Cauchy's integral formula 4.1 Introduction Cauchy's theorem is a big theorem which we will use almost daily from here on out. Right away it will reveal a number of interesting and useful properties of analytic functions. More will follow as the course progresses. If you learn just one theorem this week it should be Cauchy's integral.
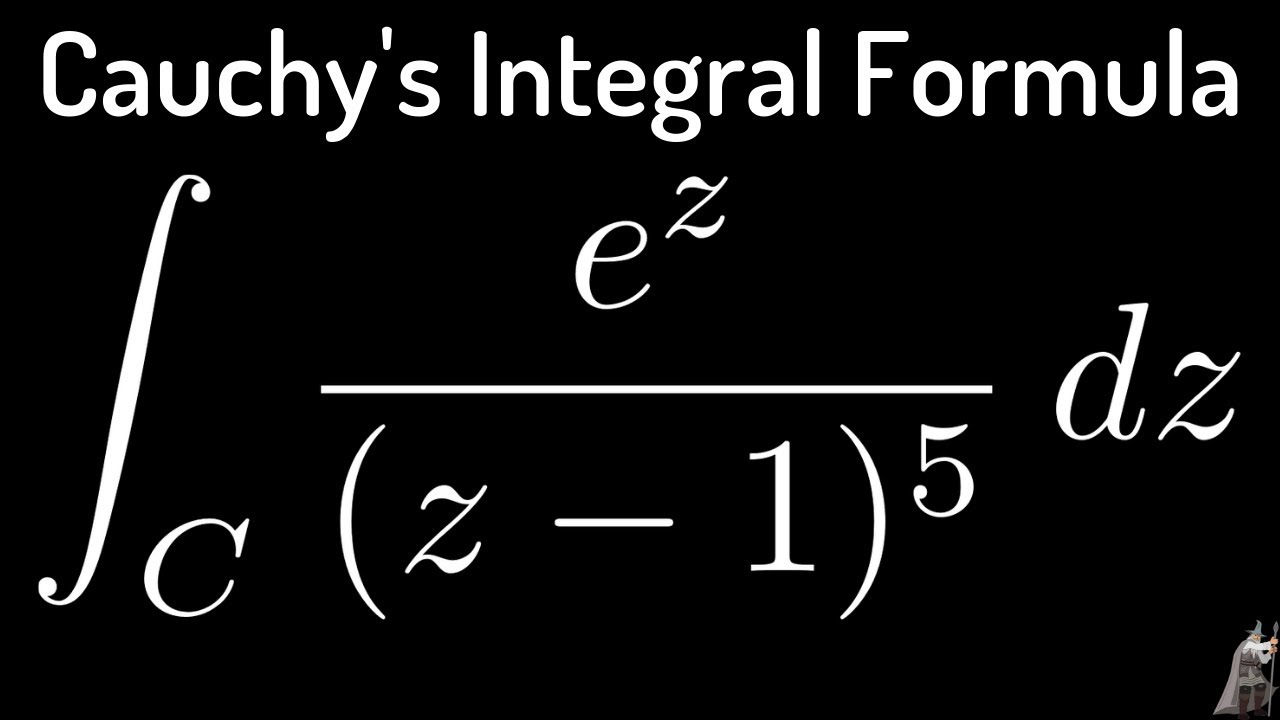
Cauchy's Integral Formula/Cauchy's Differentiation Formula used to Integrate e^z/(z 1)^5 YouTube
We may view Equation as a special instance of integrating a rational function around a curve that encircles all of the zeros of its denominator. In particular, recalling that Cauchy's Theorem, we find. ∫ q ( z) d z = ∑ j = 1 h ∑ k = 1 m j ∫ q j, k ( z − λ j) k d z = 2 π i ∑ j = 1 h q j, 1. To take a slightly more complicated.

Cauchy Integral Formula YouTube
UniversityofToronto-MAT334H1-F-LEC0101 ComplexVariables 9-Cauchy'sIntegralFormula Jean-BaptisteCampesato October14th,2020 Contents 1 Simpleconnectedness 1

Cauchy's Integral Formula with Examples Complex Integration Complex Analysis 14 YouTube
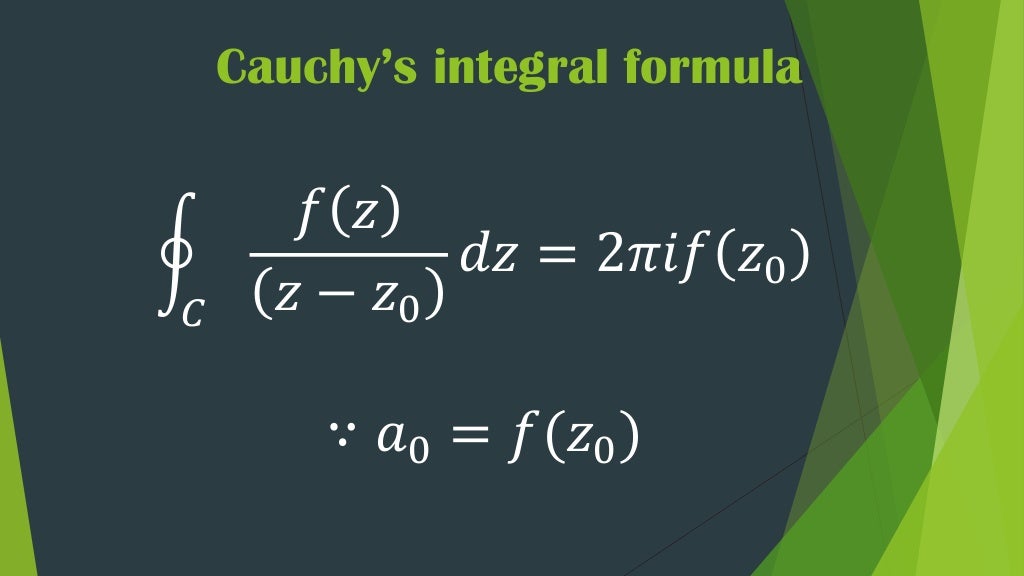
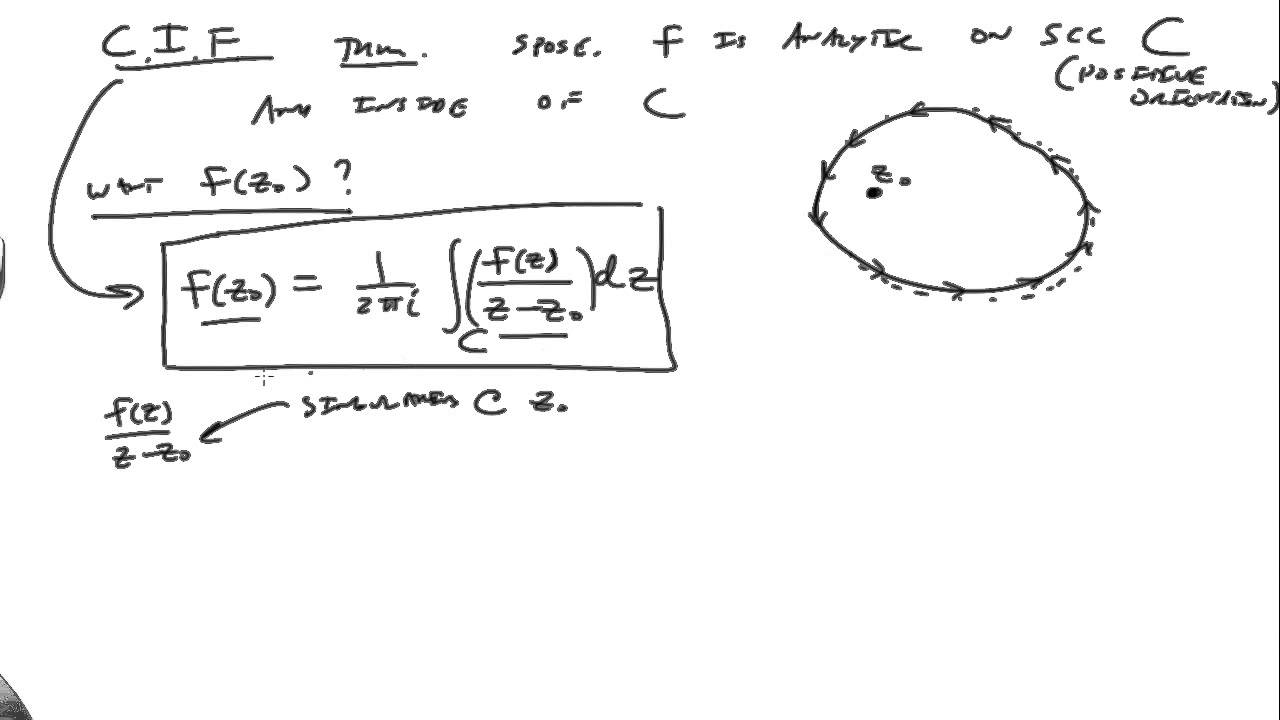
We assume C C is oriented counterclockwise. Figure 5.1.1 5.1. 1: Cauchy's integral formula: simple closed curve C C, f(z) f ( z) analytic on and inside C C. (CC BY-NC; Ümit Kaya) Then for any z0 z 0 inside C C: f(z0) = 1 2πi ∫C f(z) z −z0 dz f ( z 0) = 1 2 π i ∫ C f ( z) z − z 0 d z. This is remarkable: it says that knowing the.

cauchy integral theorem Liberal Dictionary
Cauchy's integral formula states that f(z_0)=1/(2pii)∮_gamma(f(z)dz)/(z-z_0), (1) where the integral is a contour integral along the contour gamma enclosing the point z_0. It can be derived by considering the contour integral ∮_gamma(f(z)dz)/(z-z_0), (2) defining a path gamma_r as an infinitesimal counterclockwise circle around the point z_0, and defining the path gamma_0 as an arbitrary.

Cauchy's Integral Formula 1, Proof YouTube
Cauchy's Integral Formula is a fundamental result in complex analysis.It states that if is a subset of the complex plane containing a simple counterclockwise loop and the region bounded by , and is a complex-differentiable function on , then for any in the interior of the region bounded by , . Proof. Let denote the interior of the region bounded by .Let denote a simple counterclockwise loop.

Cauchy integral formula 4 examples YouTube
Cauchy's Integral Formula. Let z0 ∈ C and r > 0. Suppose f (z) is analytic on the disk. = {z : |z − z0| < r}. Then: Essential to the proof was the following result. Let Ω ⊂ C be a domain and let f : Ω → C be analytic. If R is a closed rectangular region in Ω, then f (z) dz = 0.

Cauchy integral formula in complex plane. Download Scientific Diagram
Cauchy's integral formula is a central statement in complex analysis in mathematics. It expresses that a holomorphic function defined on a disk is determined entirely by its values on the disk boundary. For all derivatives of a holomorphic function, it provides integration formulas. Also, this formula is named after Augustin-Louis Cauchy.

An example of Cauchy's Integral Formula Solveforum
The Cauchy integral formula states that the values of a holomorphic function inside a disk are determined by the values of that function on the boundary of the disk. More precisely, suppose f: U \to \mathbb {C} f: U → C is holomorphic and \gamma γ is a circle contained in U U. Then for any a a in the disk bounded by \gamma γ,

Complex Integrals(Cauchy's theorem & Cauchy's Formula) YouTube
In applications, the boundary is often only piecewise smooth, and again that is all we need for Stokes. Theorem 4.1. 1: Cauchy-Pompeiu. Let U ⊂ C be a bounded open set with piecewise- C 1 boundary ∂ U oriented positively (see appendix B ), and let f: U ¯ → C be continuous with bounded continuous partial derivatives in U.
cauchy integral theorem Liberal Dictionary
Proof of Cauchy's integral formula. We reiterate Cauchy's integral formula from Equation 5.2.1: f(z0) = 1 2πi ∫C f(z) z −z0 dz f ( z 0) = 1 2 π i ∫ C f ( z) z − z 0 d z. Proof P r o o f. (of Cauchy's integral formula) We use a trick that is useful enough to be worth remembering. Let.
Cauchy's integral formula
This page titled 5.2: Cauchy's Integral Formula for Derivatives is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Jeremy Orloff (MIT OpenCourseWare) via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the LibreTexts platform; a detailed edit history is available upon request.
Cauchy integral formula YouTube
Chapter & Page: 15-4 Cauchy Integral Theorems and Formulas and, thus, equation (15.2) reduces to I C f (z)dz = − ZZ S 0dA + i ZZ S 0dA = 0 . Since every closed curve can be decomposed into a bunch of simple closed curves, the above
Cauchy Integral Formula 1/4 YouTube
In mathematics, Cauchy's integral formula, named after Augustin-Louis Cauchy, is a central statement in complex analysis. It expresses the fact that a holomorphic function defined on a disk is completely determined by its values on the boundary of the disk, and it provides integral formulas for all derivatives of a holomorphic function.

Cauchy Integral Formula Cauchy Theorem Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 1919090525 Shutterstock
Cauchy integrals are thus characterized by two conditions: 1) they are evaluated along a closed, smooth (or, at least, piecewise-smooth) curve $ L $; and 2) their integrands have the form. $$ \frac {f ( \zeta ) } {2 \pi i ( \zeta - z) } , $$. where $ \zeta \in L $ and $ f (z) $ is a regular analytic function on $ L $ and in the interior of $ L $.