Ernest Rutherford (1911) HISTORY OF THE ATOM
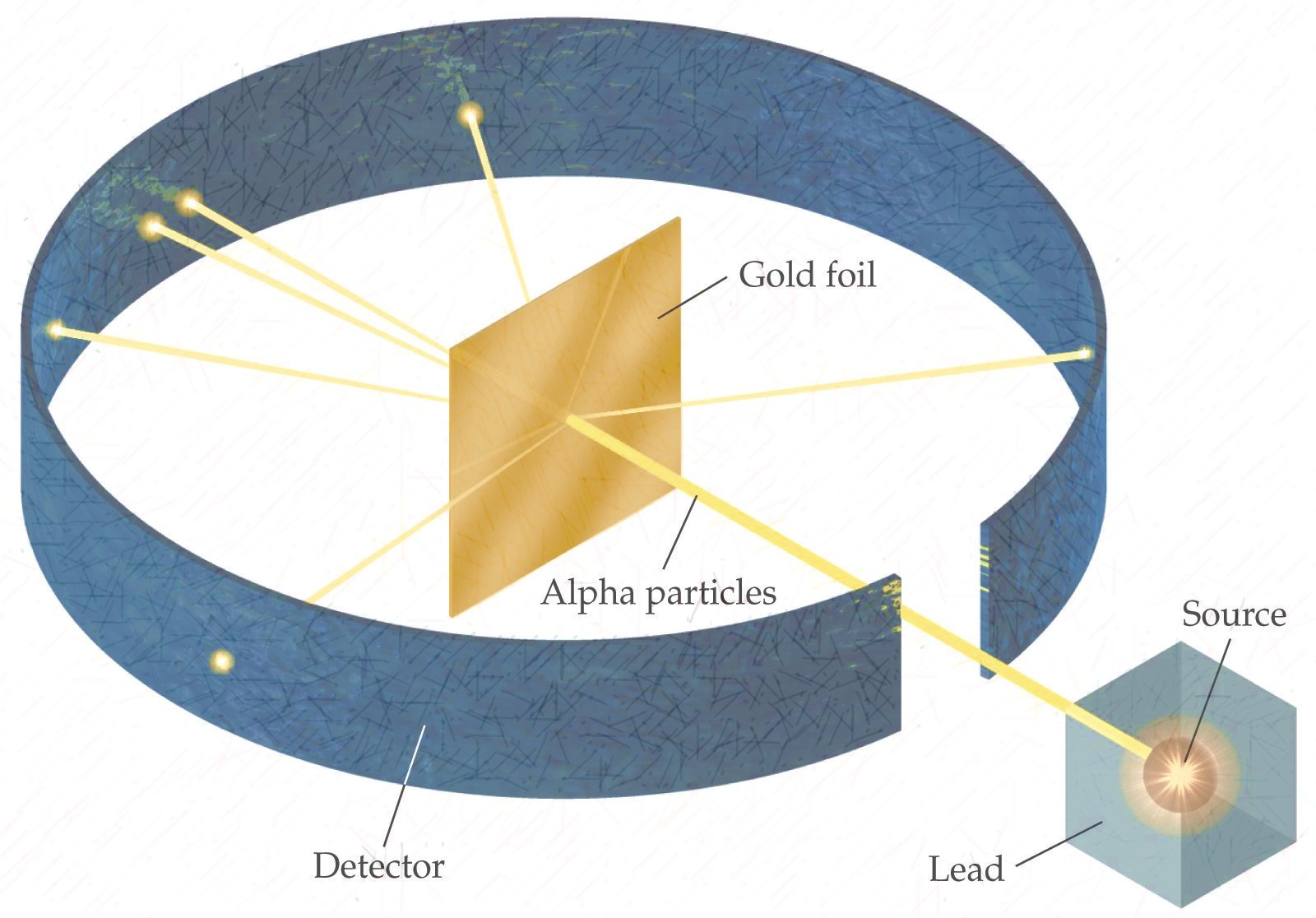
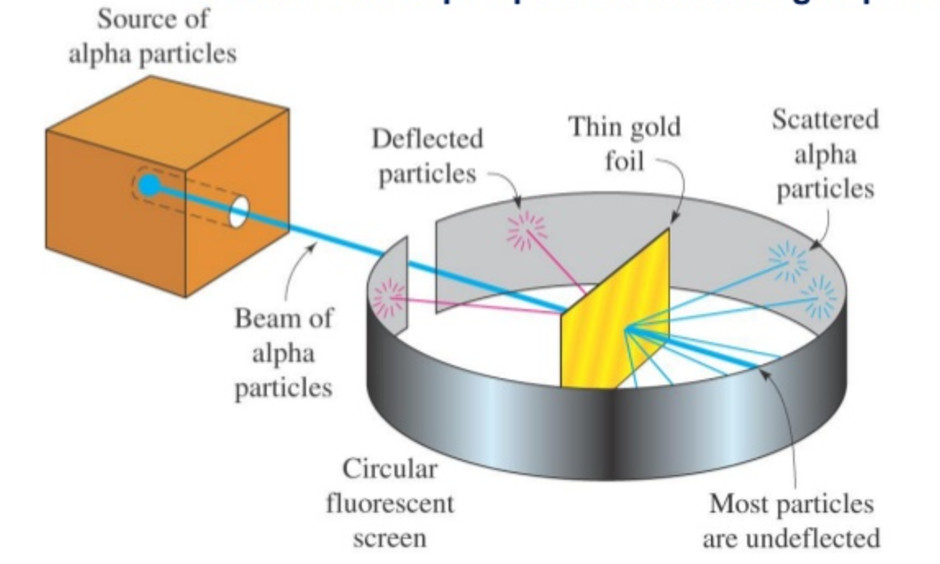
Rutherford designed an experiment to use the alpha particles emitted by a radioactive element as probes to the unseen world of atomic structure. If Thomson was correct, the beam would go straight through the gold foil. Most of the beams went through the foil, but a few were deflected.

Atomic Models Definitions, Types & Demerits Embibe
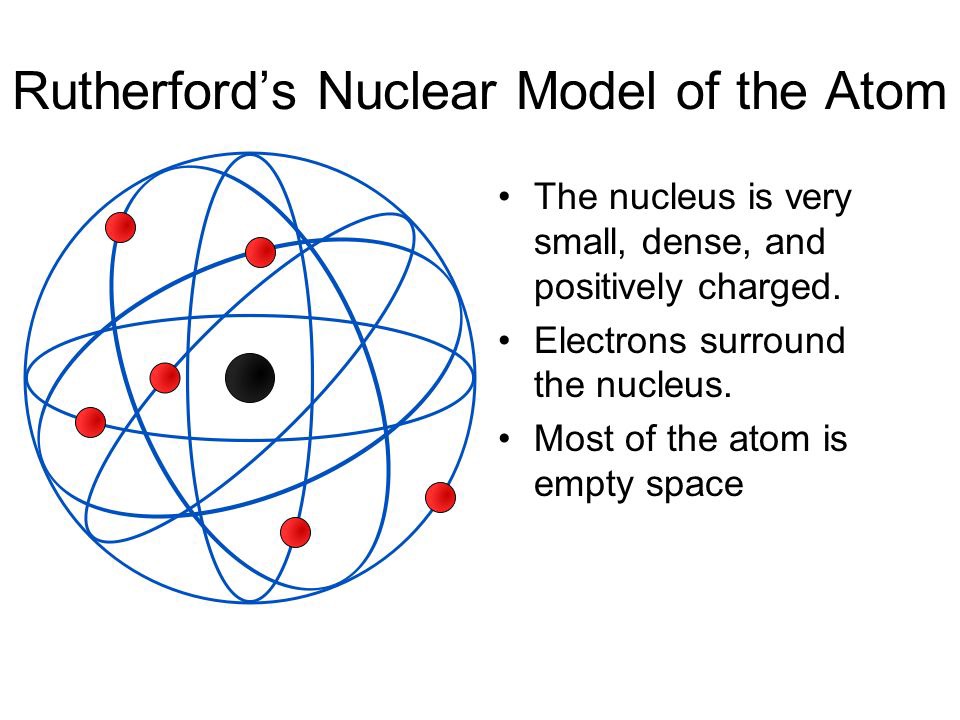
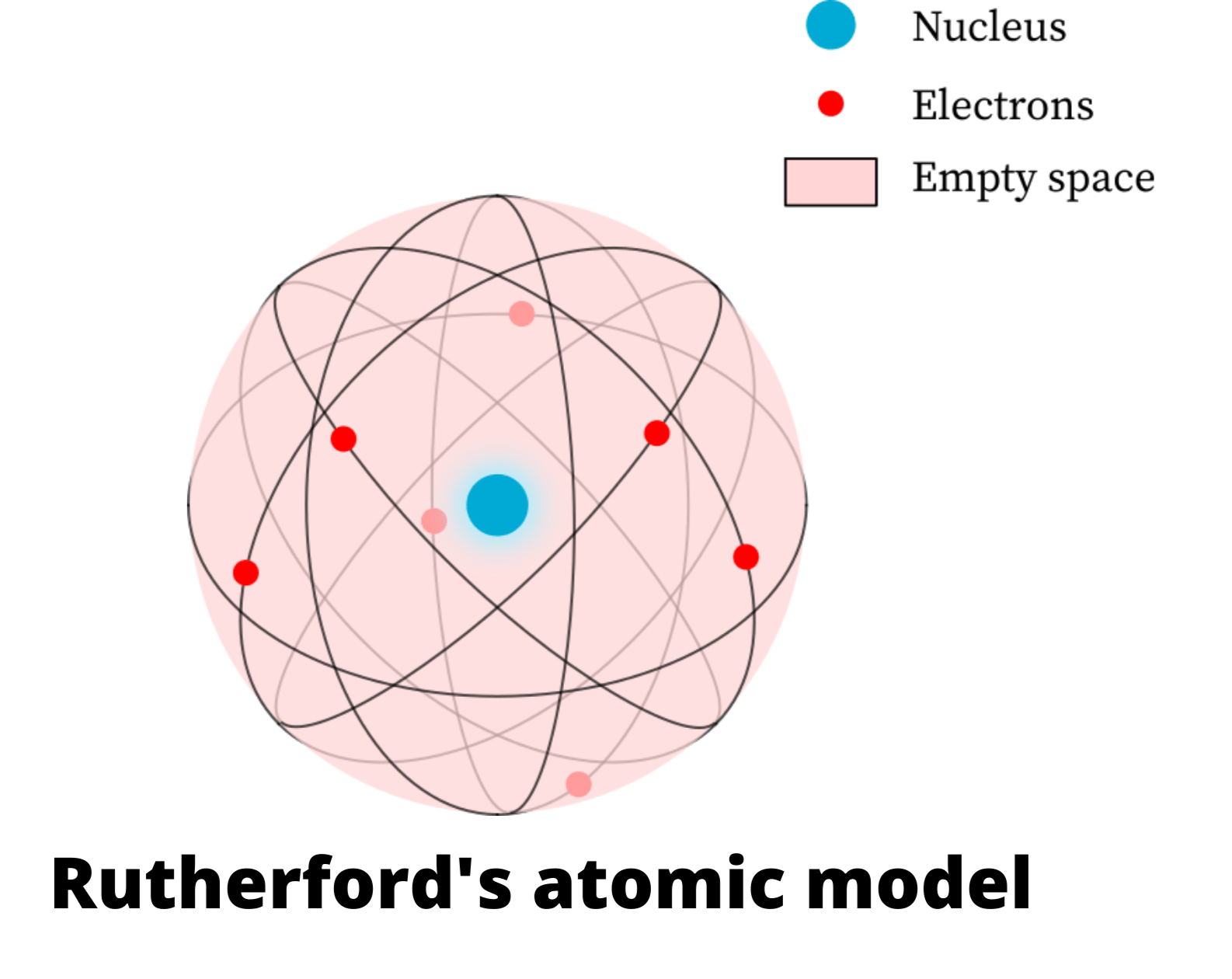
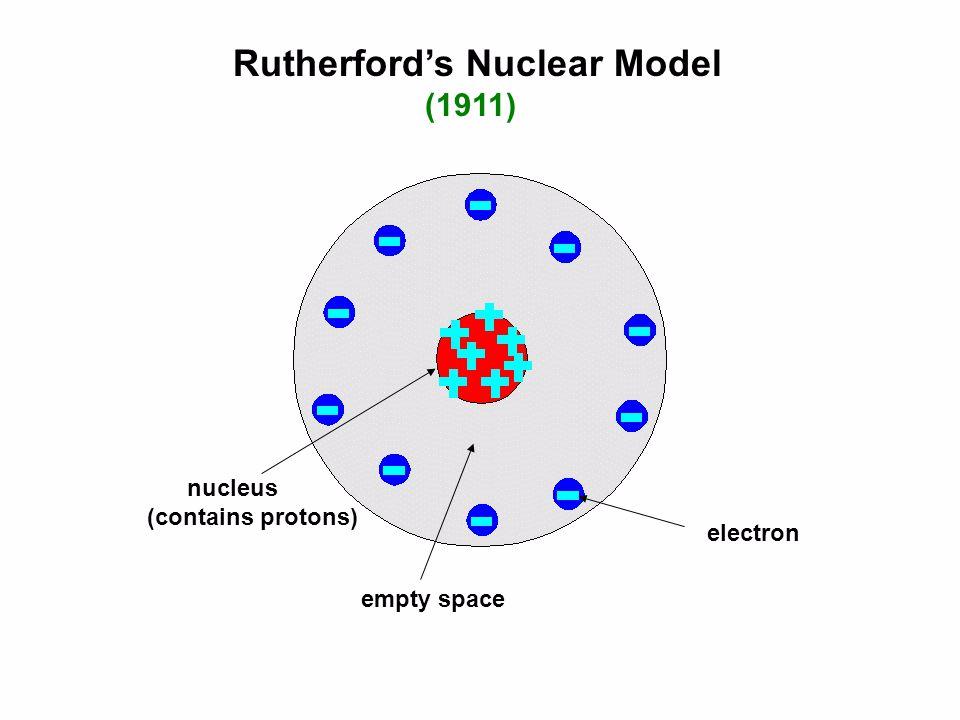
This led Rutherford to propose the nuclear model, in which an atom consists of a very small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by the negatively charged electrons. Based on the number of α particles deflected in his experiment, Rutherford calculated that the nucleus took up a tiny fraction of the volume of the atom.
Rutherford's nuclear model Sutori
Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, OM, PRS, HonFRSE [7] (30 August 1871 - 19 October 1937) was a New Zealand physicist who was a pioneering researcher in both atomic and nuclear physics. Rutherford has been described as "the father of nuclear physics", [8] and "the greatest experimentalist since Michael Faraday ". [9]

Atomic Structure & The Changing Models of Atom
Rutherford's Experiment. In the early 1900's, the plum pudding model was the accepted model of the atom. Proposed in 1904 by J. J. Thomson, the model suggested that the atom was a spherical ball of positive charge, with negatively charged electrons scattered evenly throughout.

WHAT WAS THE RUTHERFORD’S ATOMIC MODEL? JustScience Atom
In 1913, just two years after the Rutherford atomic model had been introduced, Danish physicist Niels Bohr, a student of Rutherford's, proposed his quantized shell model of the atom (see Bohr model) to explain how electrons can have stable orbits around the nucleus. The motion of the electrons in the Rutherford model was unstable because.

Atom Rutherford’s nuclear model Britannica
Rutherford's Failed Planetary Atom. There are some basic problems with the Rutherford model. The Coulomb force that exists between oppositely charge particles means that a positive nucleus and negative electrons should attract each other, and the atom should collapse. To prevent the collapse, the electron was postulated to be orbiting the.

Timeline of the Atom Ernest Rutherford 1911, 1915, 1918
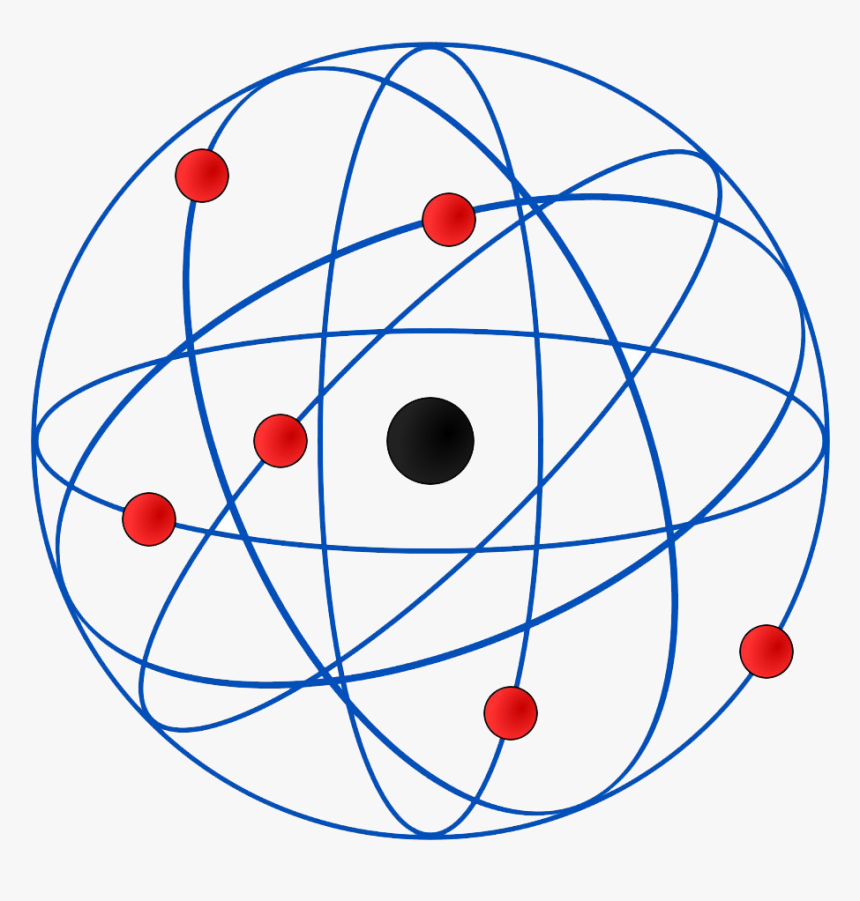
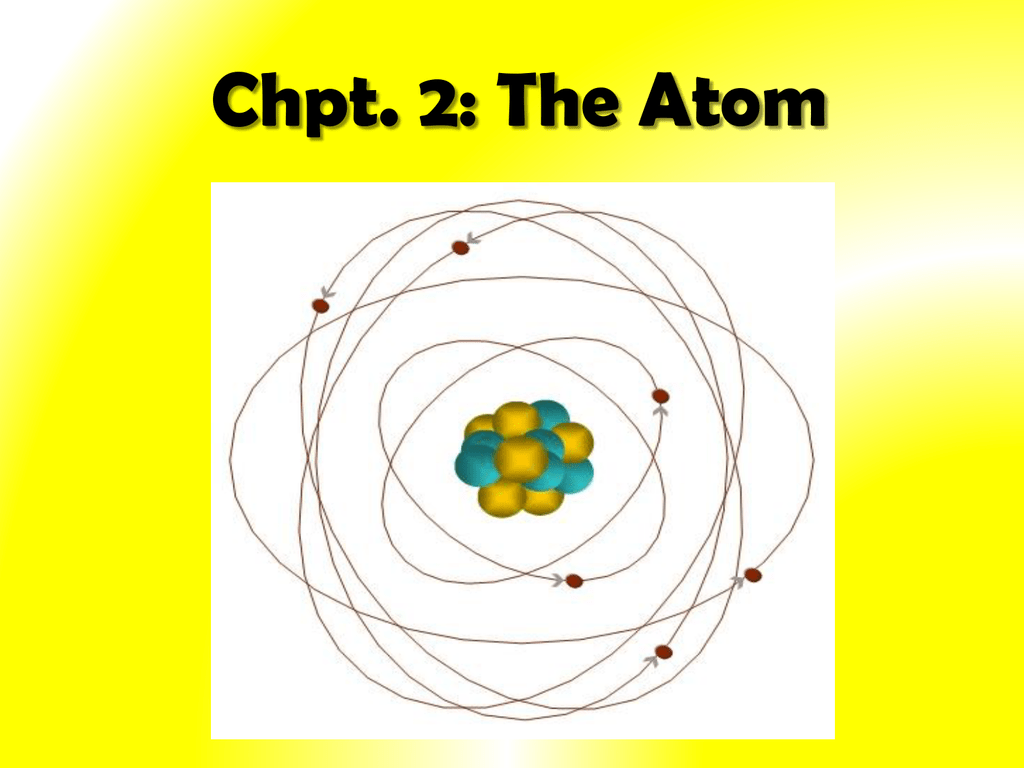
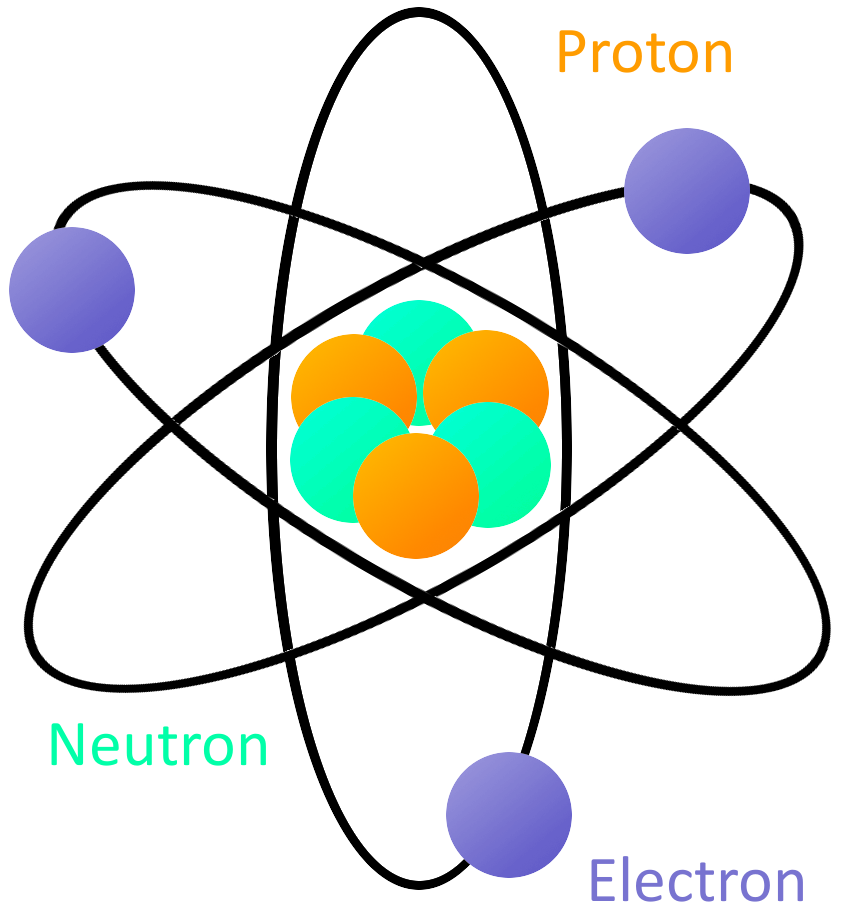
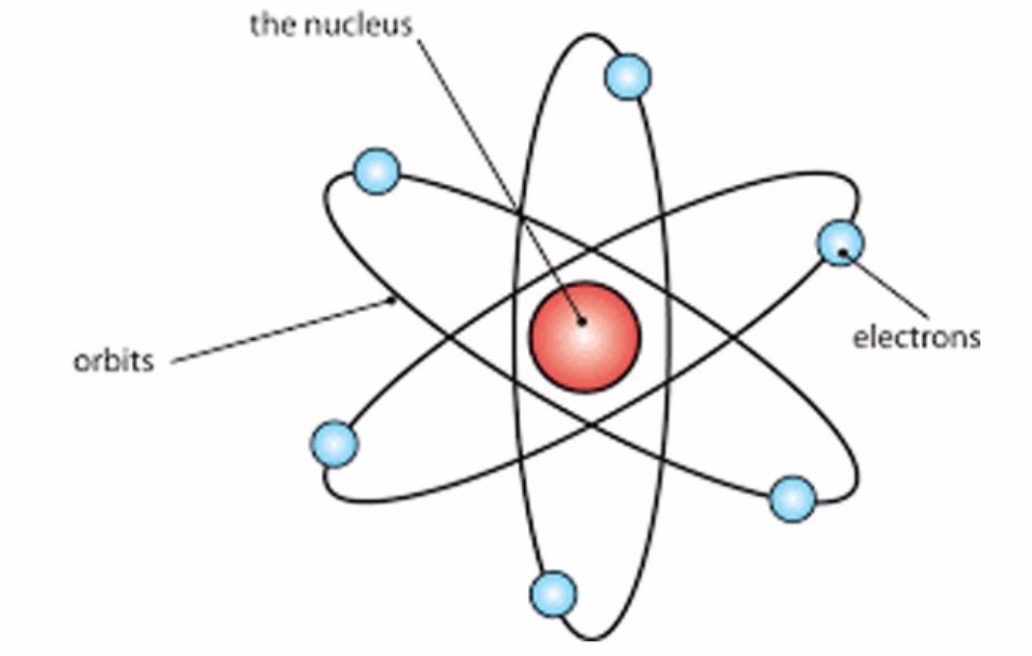
The Rutherford atomic model has 2 main parts: the nucleus, and the atom's remaining space, occupied by electrons. According to the model, the nucleus is a very small portion of the atom's volume. It occupies a small space in the very center of the atom. Protons and neutrons make up the nucleus and define the atom's chemical properties.
Rutherford's atomic model experiment, postulates, limitations & examples
Rutherford and the nucleus - Models of the atom - AQA - GCSE Combined Science Revision - AQA Trilogy - BBC Bitesize Home Learn Support Careers My Bitesize More England Early years KS1 KS2 KS3.
Rutherford Atomic Model
Ernest Rutherford, a British scientist conducted an experiment and based on the observations of this experiment, he explained the atomic structure of elements and proposed Rutherford's Atomic Model. Table of Contents Rutherfords Alpha Scattering Experiment Observations of Rutherford's Alpha Scattering Experiment Rutherford Atomic Model
Atom Png Image File Transparent Rutherford Atomic Model, Png Download
The Rutherford model of the atom is a model of the atom devised by the British physicist Ernest Rutherford. Rutherford's new model for the atom is based on the experimental results obtained from the Geiger-Marsden experiments (also called the Rutherford gold foil experiment).The Geiger-Marsden experiments were performed between 1908 and 1913 by Hans Geiger (of Geiger counter fame) and.
Rutherford's Model of the Atom
Rutherford atomic model, nuclear atom, or planetary model of the atom Key People: Ernest Rutherford atom On the Web: UC Davis - The Rutherford Scattering Experiment (Jan. 03, 2024) See all related content → Top Questions What was the impact of Ernest Rutherford's theory?

Rutherford Atomic Model ChemTalk
Physicist Ernest Rutherford envisioned the atom as a miniature solar system, with electrons orbiting around a massive nucleus, and as mostly empty space, with the nucleus occupying only a very small part of the atom. The neutron had not yet been discovered when Rutherford proposed his model, which had a nucleus consisting only of protons. (more)
What is Electricity?
Rutherford's basic model by proposing that electrons had set energy levels (Fig. 7). This is the model of the atom most commonly portrayed in textbooks: a nucleus orbited by electrons at different levels. It helped solve the problem of the collapsing atom and earned Bohr a Nobel Prize. Just as Bohr built on Rutherford's model, many other
Rutherford's Model of an Atom Chemistry, Class 11, Structure of Atom
In 1911, Rutherford and coworkers Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden initiated a series of groundbreaking experiments that would completely change the accepted model of the atom. They bombarded very thin sheets of gold foil with fast moving alpha particles. Figure 3.4.2 3.4. 2 (a) The experimental setup for Rutherford's gold foil experiment: A.

Elements Clipart Atom Element Rutherford Atom Model Gif Png
Rutherford's atomic model or planetary model of the atom is a model proposed by Ernest Rutherford. In 1909 the Geiger and Marsden experiment was performed, also known as the Rutherford experiment, as it was led by Rutherford himself. The Rutherford scattering observed in the investigation suggested that the early "Panettone" and "Saturnian.
Rutherford Model of an Atom Class 9, Structure of an atom
Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus of the atom in 1911. We read this in textbooks and in popular writings. But what does that statement mean? Geographical discovery usually means that one sees a place for the first time. But can discovery be the same for a realm hidden from sight? One cannot see an atom in that sense.