
44 best images about Ser y estar on Pinterest Spanish, Studentcentered resources and An adjective
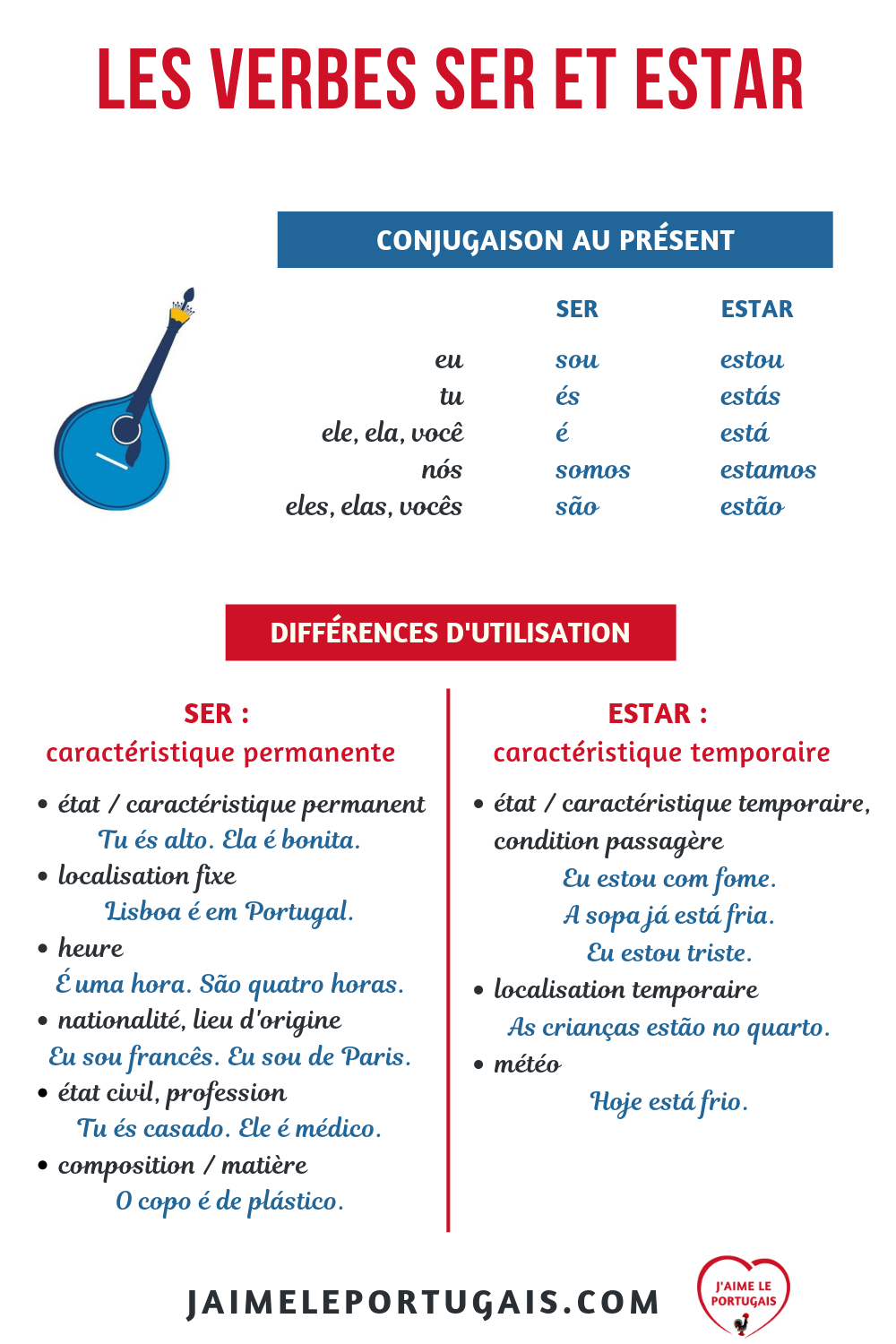
Present Tense of "Ser," "Estar," and "Tener". Quick Answer. Ser ( to be ), estar ( to be ), and tener ( to have ), three of the most frequently used verbs in Spanish, are all irregular in the present tense. The present tense conjugations for the irregular verbs ser, estar, and tener are given below, along with some examples.

SER OU ESTAR Português Ple Apostilas Aula de português, Fichas de trabalho, Atividades de
Simply put, ser is used to talk about permanent states, while estar is used to talk about temporary conditions. In English, you would use the verb "to be" for both, but in Spanish they have somewhat different meanings. Another way to explain their difference is that ser talks about what something is and estar talks about how something is.

Ser ou Estar? Les adjectifs qui changent de sens
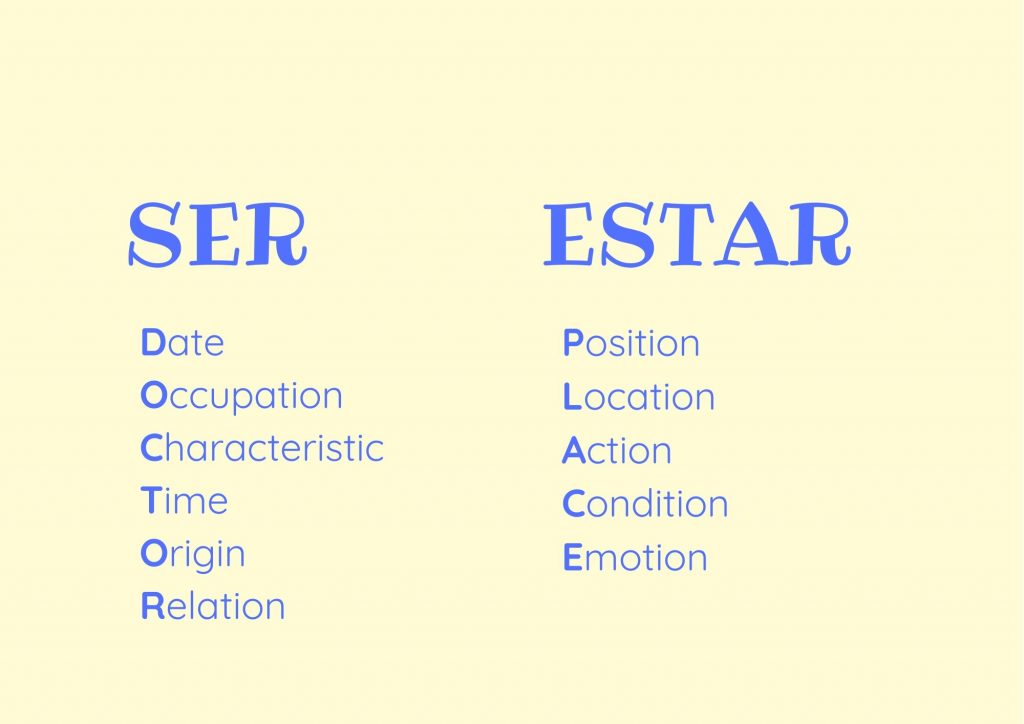
In a nutshell, the difference between ser and estar is that the first refers to permanent or lasting traits, while the latter refers to temporary conditions. Ser is used to: Identify people or things. Say the date and time. Describe people or things. Refer to the place of an event. Express origin or nationality.

Unidad Didactica Digital Español para Extranjeros USOS DE LOS VERBOS SER Y ESTAR
The English verb be has two translations in Spanish grammar: ser and estar. Ser is used for qualities and characteristics and in connection with adverbs of time. Estar describes temporary conditions, location, the present progressive. Learn the difference between ser and estar with Lingolia's online grammar rules and free exercises. Our lists help you learn which words and expressions are.
Soutien Espagnol Lycée Elisa Lemonnier Primera lección Ser y Estar
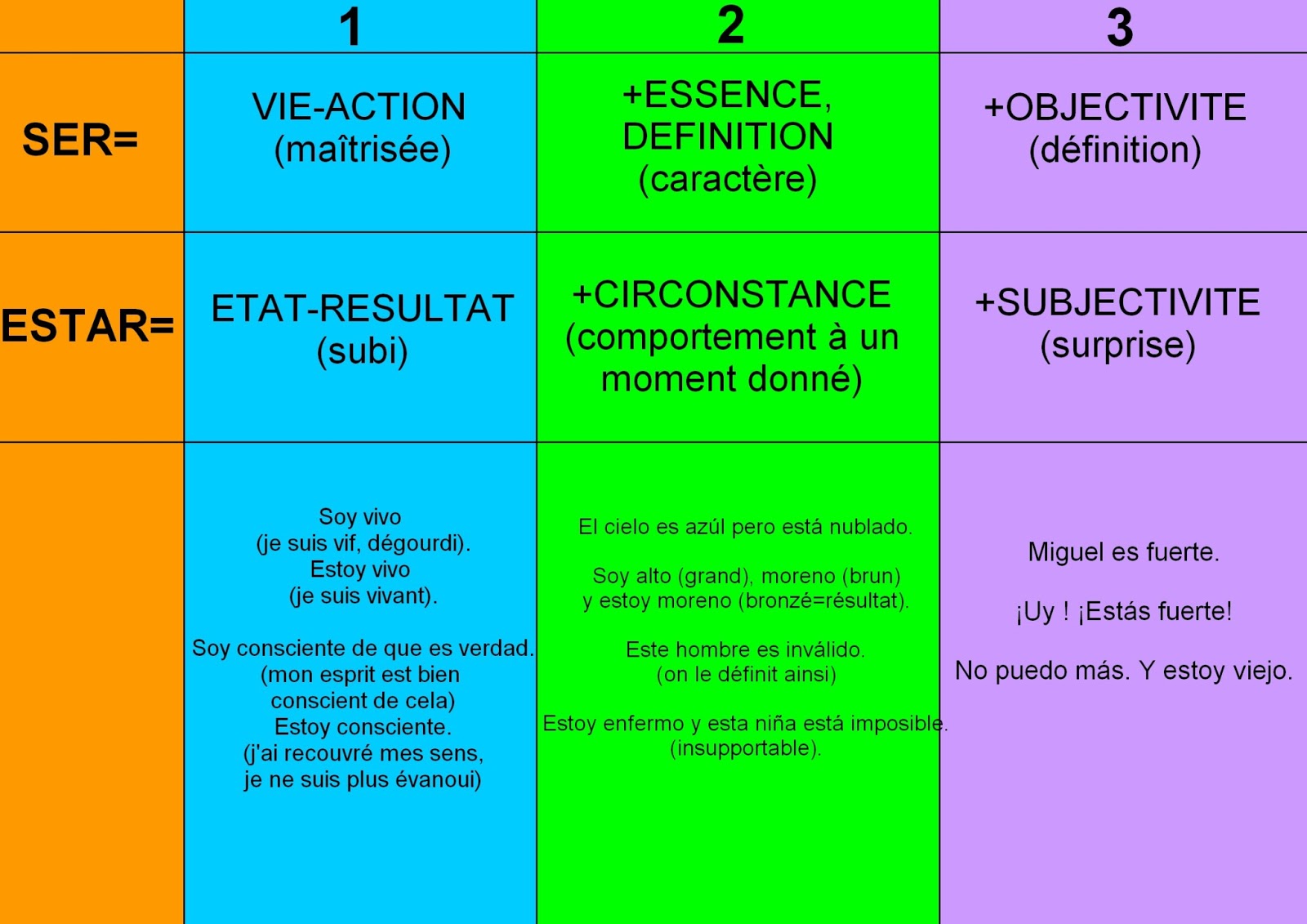
Ejemplos con el verbo Estar. En general usamos el verbo estar en las siguientes situaciones: Usamos el verbo estar para indicar una situación temporal. La situación puede ser física, mental, imaginaria o un estado de ánimo: Estoy enfermo. Estoy contento. Estás de viaje. Me gusta ver que estás bien. El libro está a la derecha de la lámpara.

The Difference Between “Ser” and “Estar”. Kids Speak Spanish in 2021 How to speak spanish
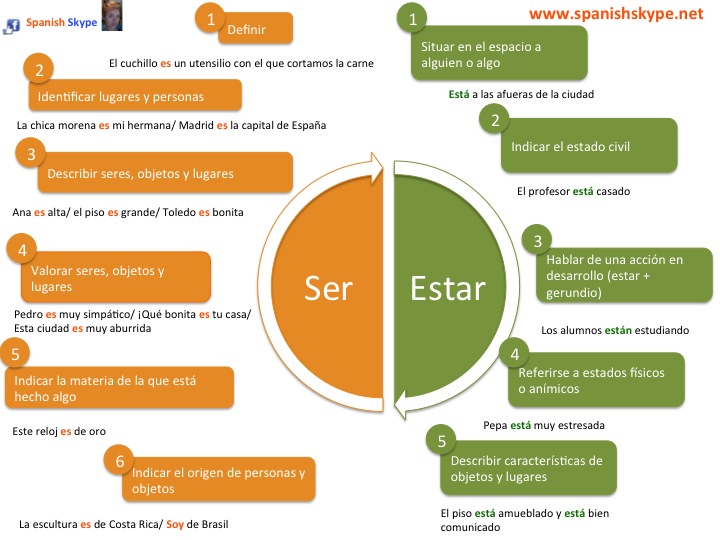
Ser ou estar? - cours 1) Le verbe SER s'emploie: a) devant un nom qui exprime une définition : esto es mi cocheça c'est ma voiture b) devant un nom qui désigne : la profession,la matière,la possessionyo soy profesorje suis professeur l'origine..Pablo es español.Pablo est espagnol
meilleur Conjuguer Ser dessin Dablog
La manzana es verde. The apple is green. (essence) Note how the adjective "verde" actually changes meaning, depending upon whether it is used with ser or estar. La manzana está verde. (condition: verde = unripe) La manzana es verde. (essential characteristic: verde = color green) To address condition, use estar. Estar is an irregular verb.

Ser Estar / There are two verbs that mean to be in spanish, ser ultimately, the best way to
Introducción. Los verbos ser y estar son el mismo verbo en otros idiomas, pero en español tienen significados distintos. A continuación te damos algunas pistas para que aprendas a diferenciarlos de forma fácil y definitiva. En la sección de ejercicios puedes poner a prueba tus conocimientos.
Ser And Estar Verb Conjugation Chart kanariyareon
Quick Answer Tricky Pairs Learning the differences between ser and estar, por and para, and the subjunctive and the indicative is often quite challenging for learners of Spanish. ¡Ánimo! ( Cheer up!) After reading this article, you'll have a good handle on the first of these tricky pairs, ser and estar.

ser estar gramatica espanola Spanish Unicorn
Complete the gaps with the correct form of ser or estar in the present tense. Esa peluquería nueva en el barrio. [That salon is new to the neighbourhood.]|how something is → ser |3rd person singular: es. Nosotros en el cine. [We are at the cinema.]|current location → estar |1st person plural: estamos. Esas joyas de mi abuela.

Portuguese Ser & Estar Aula de português, Portugues basico, Curso de portugues
Fill in the blanks by spelling out each number in Spanish. Follow the model. 1 - Números de teléfono Audio You want to invite some classmates to a party, but you don't have their telephone numbers. Listen to each person's telephone number and write what you hear. Follow the model.

20 Ser and Estar Worksheet Printable Worksheet Template Spanish learning activities, Spanish
estar Comment les conjuguer ? Quand les employer ? Le verbe ser est employé dans les cas suivants : caractéristique inhérente ou permanente d'un être (personnalité) Exemples : Félix y Raúl son altos. Antón es el más listo. information sur l'identité d'une personne (nom, nationalité, etc.) Exemples : Yo soy Santiago. Este es el Teatro Real.

Ser ou estar ne plus les confondre Artofit
Ser and estar are the two verbs most frequently used as the equivalent of the English "to be." Ser typically is used in describing the nature of someone or something. Estar typically is used in referring to a state of being that isn't necessarily innate. The Spanish verbs "ser" and "estar" both mean "to be." Here is a quick guide, including a.

SER vs ESTAR. Infografía Spanish grammar, Learning spanish, Spanish language learning
2) Le verbe estar est utilisé pour les actions qui ne durent pas ou pour situer dans l'espace . Les verbes ser et estar ont tous les deux des conjugaisons irrégulières . Le verbe SER au présent de l'indicatif Le verbe ESTAR au présent de l'indicatif SER SINGULIER 1ère pers Yo soy 2ème pers Tú eres 3ème pers Él - Ella es PLURIEL
Spanish Skype Lessons Ser y EstarSer y Estar Spanish Skype Lessons
"Ser" and "estar" allow speakers to differentiate between permanent, inherent traits and temporary, situational states. This dual structure provides a lens through which Portuguese speakers perceive and describe the world around them. For instance, consider the difference between saying "I am a teacher" and "I am tired".

Ser ou Estar? Deutsch DAF Arbeitsblätter pdf & doc
It most commonly relates to a change in physical appearance, but could also refer to demeanor, personality, or tastes, for example. It can be positive or negative. Here are a few more examples: Permanent (or at least long-term) personality traits: muito tímido. médica. Temporary physical states: Temporary emotional traits: muito nervoso, relaxa!