The Superficial Muscles of a Cow ClipArt ETC
1, masseter muscle; 2, coronoid process; 3, temporal fossa; arrowheads, temporal line; 4, paracondylar process; 5, occipital condyle; 6-9 cheek teeth (Triadan numbers).. Figure 25-18 Left half of upper and right half of lower jaw of cow. Note the different shapes of the upper and lower cheek teeth and the large diastema (1).

Bovine Cow Muscle Anatomy Poster Muscle anatomy, Large animal vet, Anatomy
5 Muscles of the Forelimb 5.1 Extrinsic Musculature 5.2 Intrinsic Musculature 6 Muscles of the Shoulder 6.1 1. Lateral 6.2 2. Medial 6.3 3. Caudal (Flexors) 7 Muscles of the Elbow 7.1 Extensors 7.2 Flexors 8 Muscles of the Carpal and Digital Joints 8.1 Extensors 8.2 Flexors 9 Vasculature of the Forelimb 10 Webinars

MODEL OF A COW'S ANATOMY, THE MUSCLES, FRAGONARD MUSEUM, NATIONAL VETERINARY SCHOOL OF ALFORT
A baby cow is called a calf. A female calf is sometimes called a heifer calf and a male a bull calf. A heifer is a female that has not had any offspring. The term usually refers to immature females; after giving birth to her first calf, however, a heifer becomes a cow. An adult male is known as a bull.

ArtStation Cow anatomy sceleton muscles ligaments
The subiliac lymph nodes (bov) are found at the cranial edge of the thigh muscles, about midway between the tuber coxae and the fold of the flank. (Fig. 31.10) The paralumbar fossa (ID in bov, but also in eq) is the most common surgical site for entry into the ruminant abdomen.

Pin by Tapio Terävä on Cow/Bull Reference Animals, Muscular system, Bovine
norecopa.no NORINA Bovine Anatomy: The Cow Anatomical Chart Bovine Anatomy: The Cow Anatomical Chart This chart shows views of the cow's left lateral view with the dorsal and vertebral regions indicated. Type of record: Chart/Diagram. Category: Anatomy
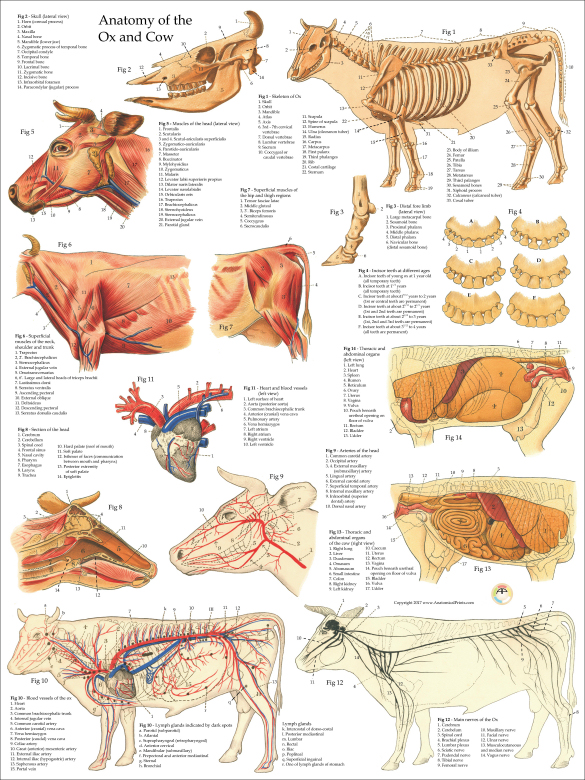
Cow Ox Anatomy Poster
Muscles of the hindlimb of a cow Cow anatomy organs Digestive organs of a cow Cow anatomy stomach Compartments of cow stomach Liver and pancreas of cow anatomy Organs of the respiratory system from a cow Lung anatomy of a cow Heart of a cow Cow hoof anatomy Cow anatomy labeled diagram Frequently asked questions on cow Conclusion Cow anatomy

Cow Bovine Veterinary Muscles Anatomy Chart Poster Zazzle
Cow yoga pose stretches and warms up the following muscles: Hip flexors. Cow pose stretches your hip flexors, making them longer and less prone to injury. There are five muscles involved in.
.jpg)
Superficial muscle of cow head and neck plastinated specimen, medical specimens
The Anatomy of a Cows Stomach. Inside a cows stomach region, there are 4 digestive departments:. 1. The Rumen - this is the largest part and holds upto 50 gallons of partially digested food. This is where the 'cud' comes from. Good bacteria in the Rumen helps soften and digest the cows food and provides protein for the cow.

Bovine Muscle Anatomy Cow Muscular System Cow muscles by uberkudzu Animals Muscular system
Conclusion Cow muscle anatomy Muscles are the contractile organs that are responsible for the movement of the cow's body. You will find two major types of muscles in the cow muscle anatomy - striated and nonstriated. Here, the striated muscles of a cow include skeletal and cardiac muscle, whereas the nonstriated muscles include smooth muscle.
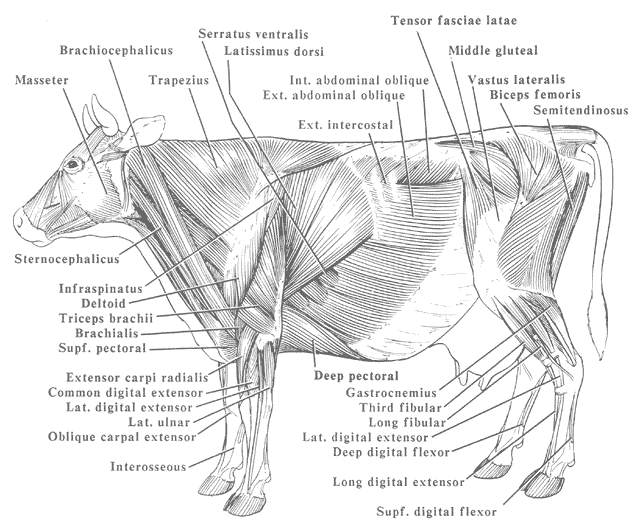
Muscular System Of A Cow paradetips
The muscles of the shoulder include the deltoid muscles, teres major, teres minor, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis and coracobrachialis. These muscles provide flexion and stability to the shoulder joint. The elbow joint extensors include the triceps brachii and the tensor fasciae antebrachii.
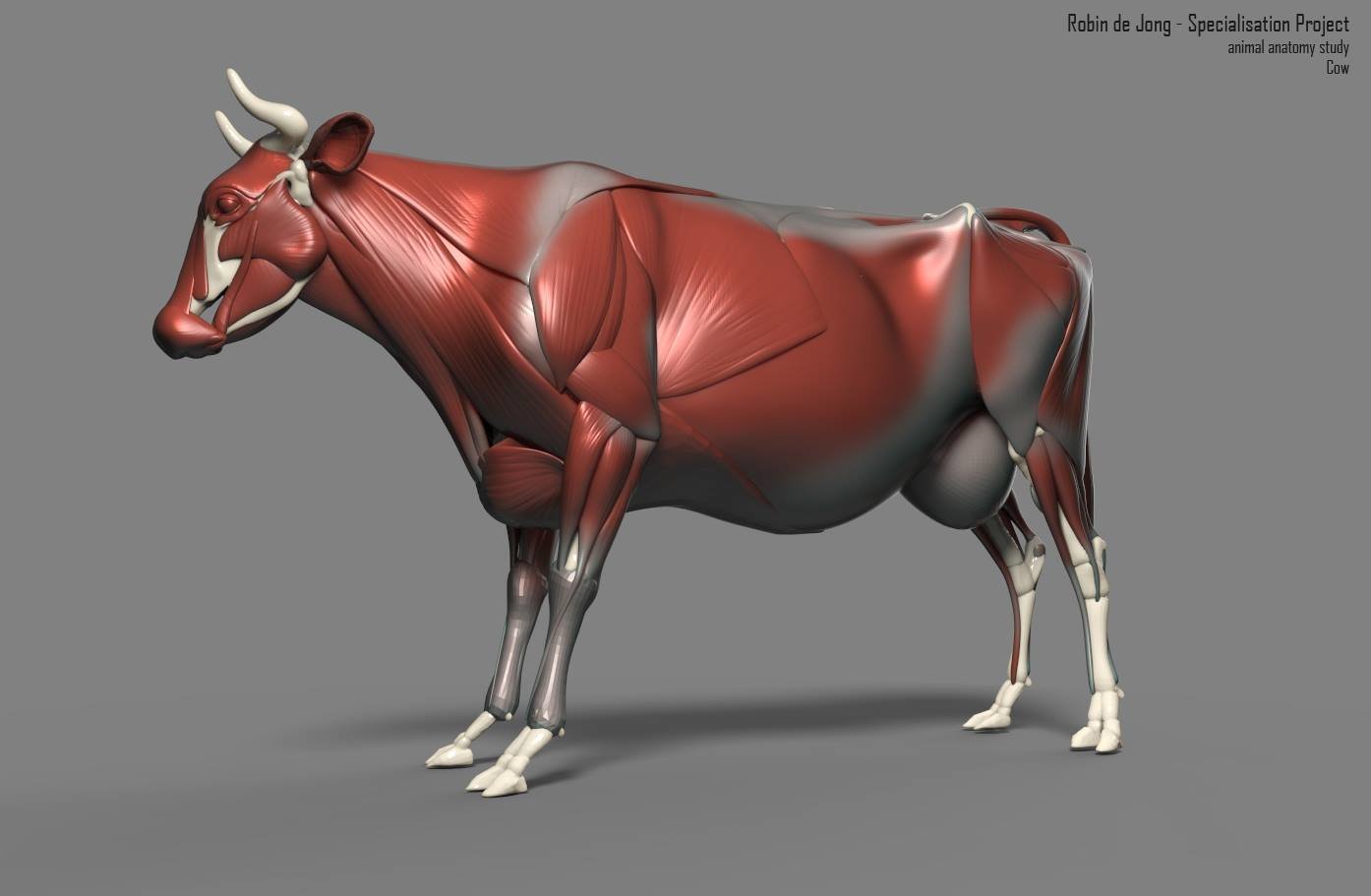

Robin de Jong cow anatomy study
Beef Stats. The U.S. plays a major role in the beef industry! 50%. A 3oz serving of beef supplies 50% of the Daily Value for protein. 2nd. The Infraspinatus muscle of the Flat Iron Steak is the second most tender muscle in the beef carcass. 130 Million. More than 130 million pounds of Flat Iron and Petite Tender combined were sold in retail and.
Anatomy
Delayed treatment or unresponsiveness to treatment in cows with clinical periparturient hypocalcemia ( milk fever ), as well as calving paralysis from nerve injury after dystocia, may result in prolonged involuntary recumbency. Less common primary causes of recumbency in alert downer cows include severe hypokalemia and possibly hypophosphatemia .

Muscle Groups of Cattle Diagram Quizlet
1 Pelvic Girdle and Hip 1.1 Bones 1.1.1 Bovine Bone Specifics 2 Joints and Synovial Structures 2.1 Sacroiliac Joint 2.2 Coxafemoral/Hip Joint 3 Musculature 4 Proximal Hindlimb including Stifle and Tarsus 4.1 Bones 4.1.1 Bovine Bone Specifics 4.2 Joints and Synovial Structures 4.3 Musculature 5 Vasculature of the Hindlimb 6 Webinars

Allgemeine Anatomie des Bullen und der Kuh Bildatlas
Dairy cows are judged on, and selected for, wide spread pin bones. (In the HORSE, the tuber ischii are covered by hamstring muscles.) The head of the femur, which articulates with the acetabulum, is found medially, while on the lateral side there is the greater trochanter with cranial and caudal cusps. (Figs. 4-3 and below)

Merck Veterinary Manual, what a great reference! Musculoskeletal system, Veterinary, Merck
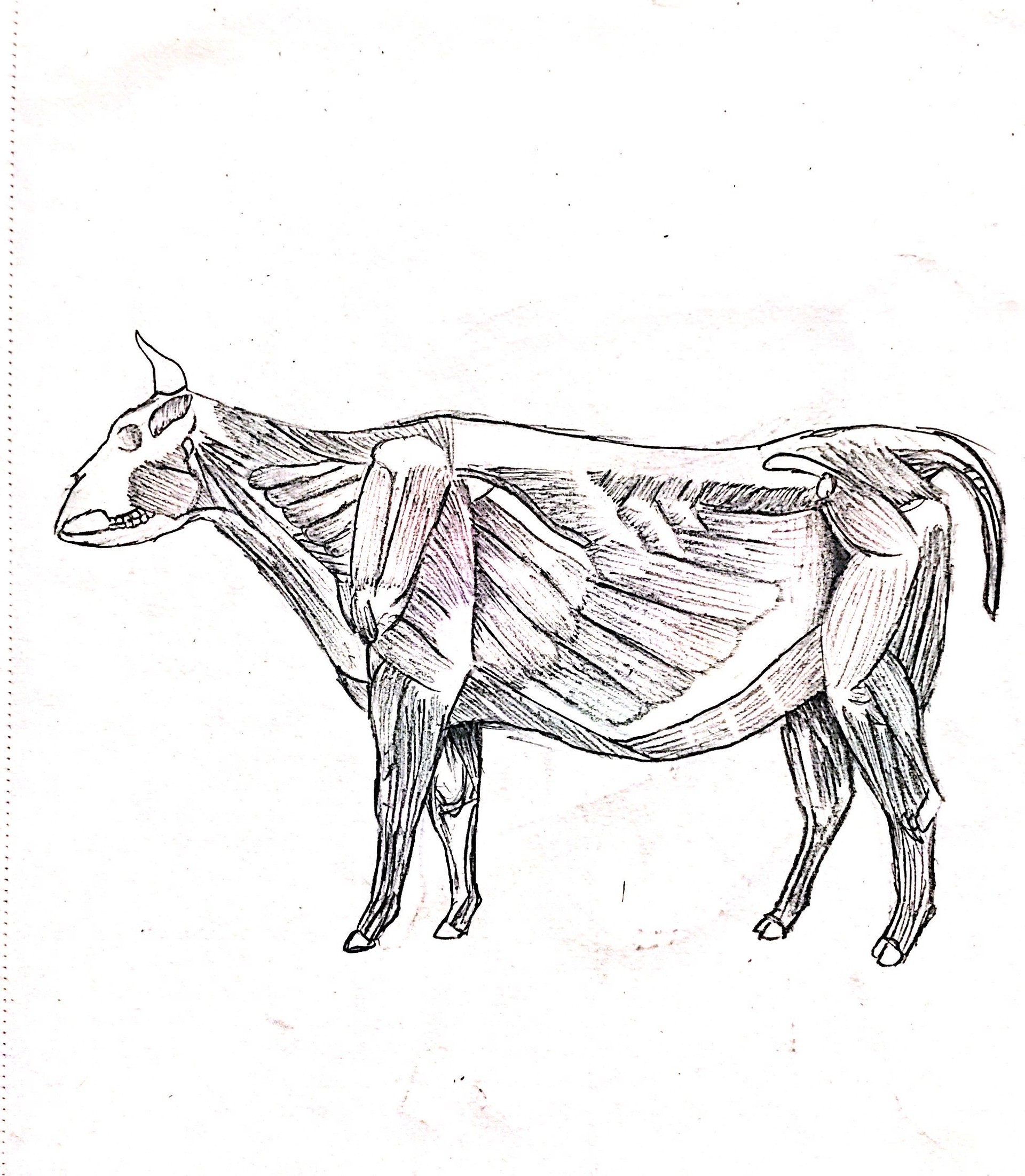
The superficial muscles of a cow are diagramed. Labels: 1, Occipito-Frontalis. 2, Orbicularis Palpaebrarum. 3, Masseter. 5, Sterno-cleido-Mastoid. 6, Trapezius. 7, Latissimus Dorsi. 8, Pectoralis. 9, 10, External and Internal oblique muscles. 11, Opening of the mammary artery and vein (milk vein). 12, Gluteii. 13, Rectus Femoris muscle.
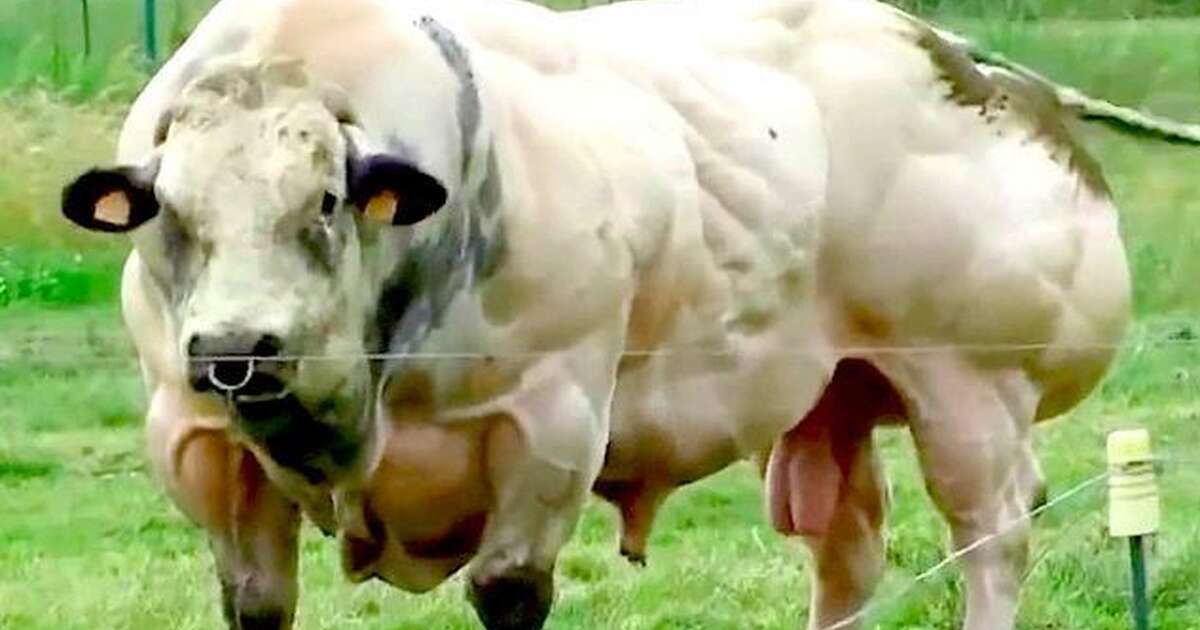

The Reason This Cow Is So Insanely Muscular The Dodo
Muscle Descriptions. Contact. Michaella Fevold, Assistant Professor of Practice Animal Science Department A213c Animal Science Building Lincoln, NE 68583-0908 (402)472-9896. [email protected]. Related Links. Beef Research; Beef Nutrition; Beef Innovations Group; Beef for Foodservice; Beef for Retail;