
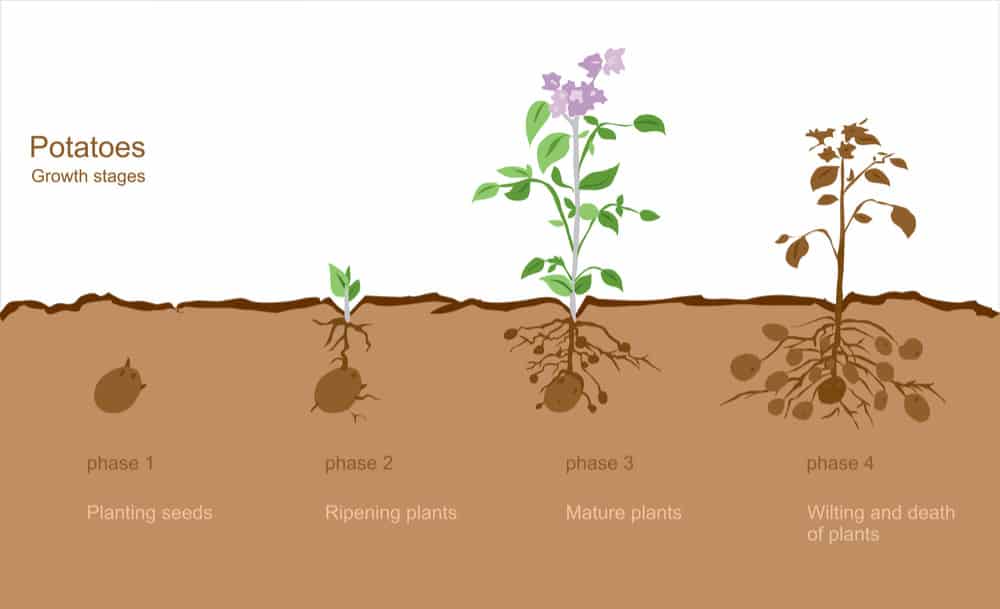
Understanding various growth stages of a potato plant
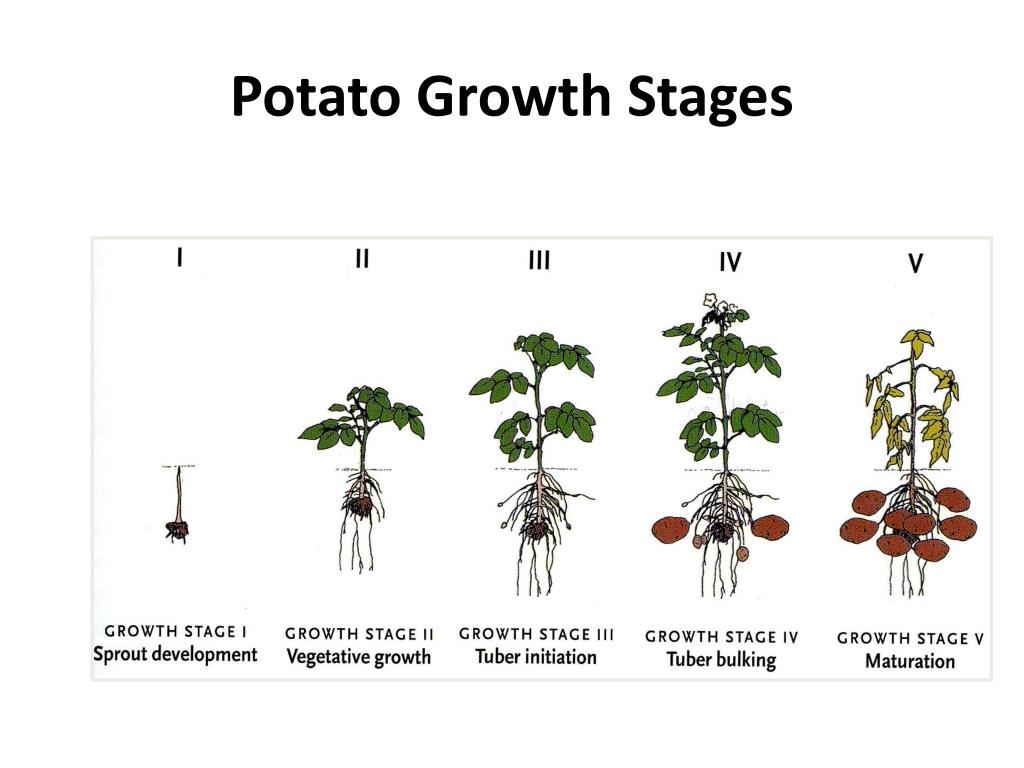
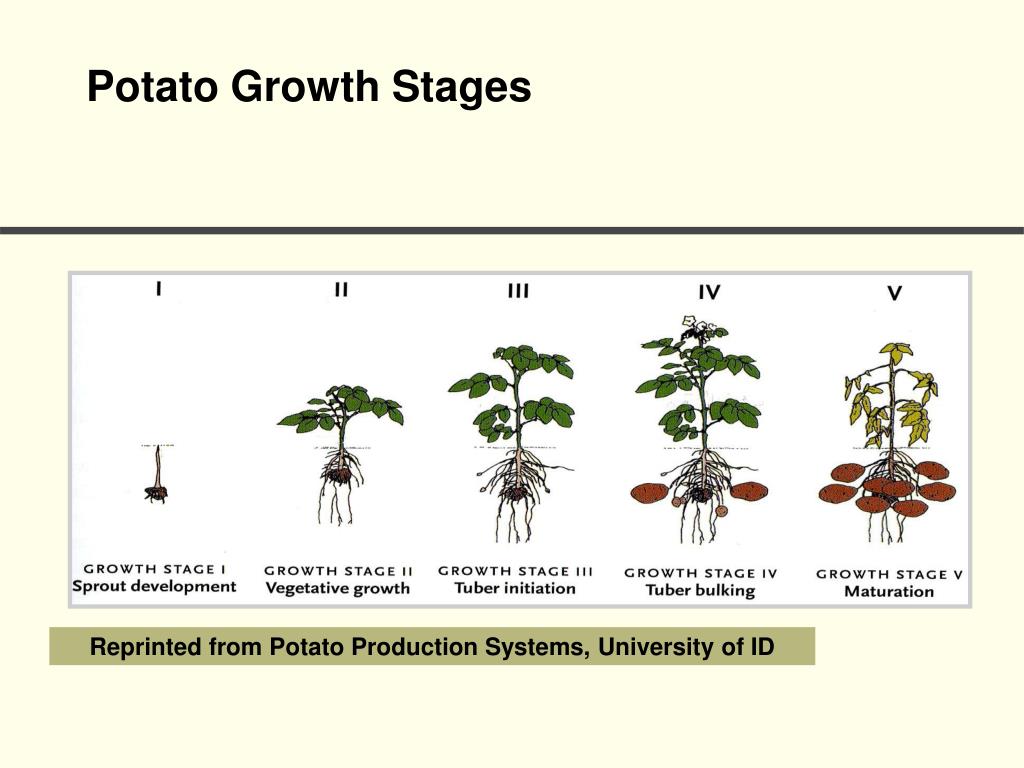
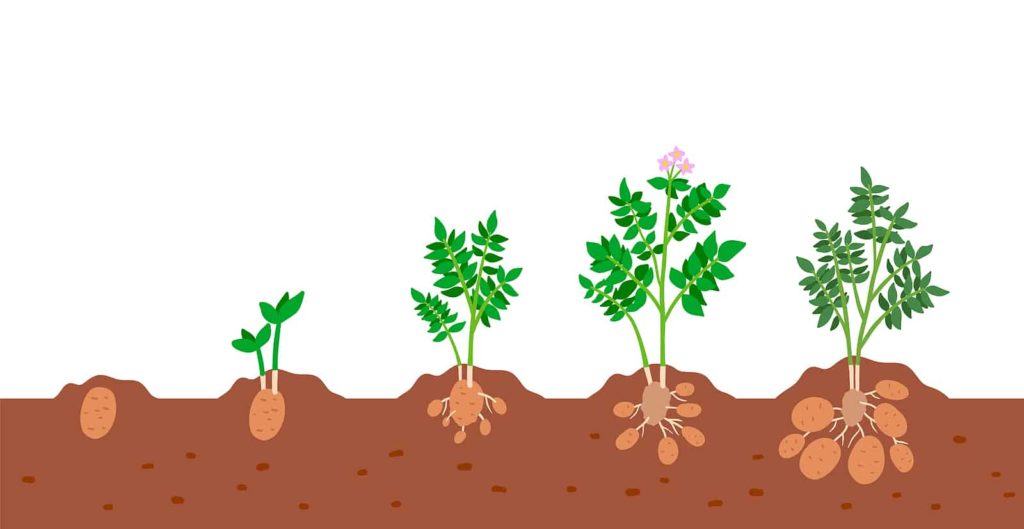
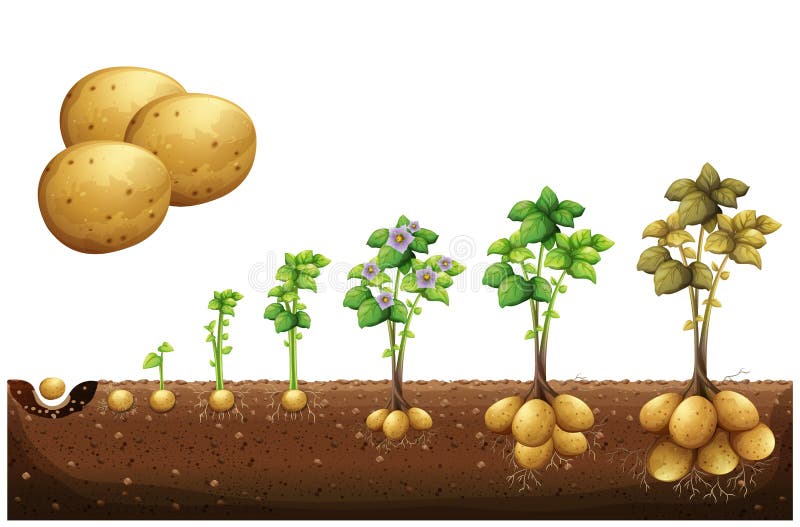
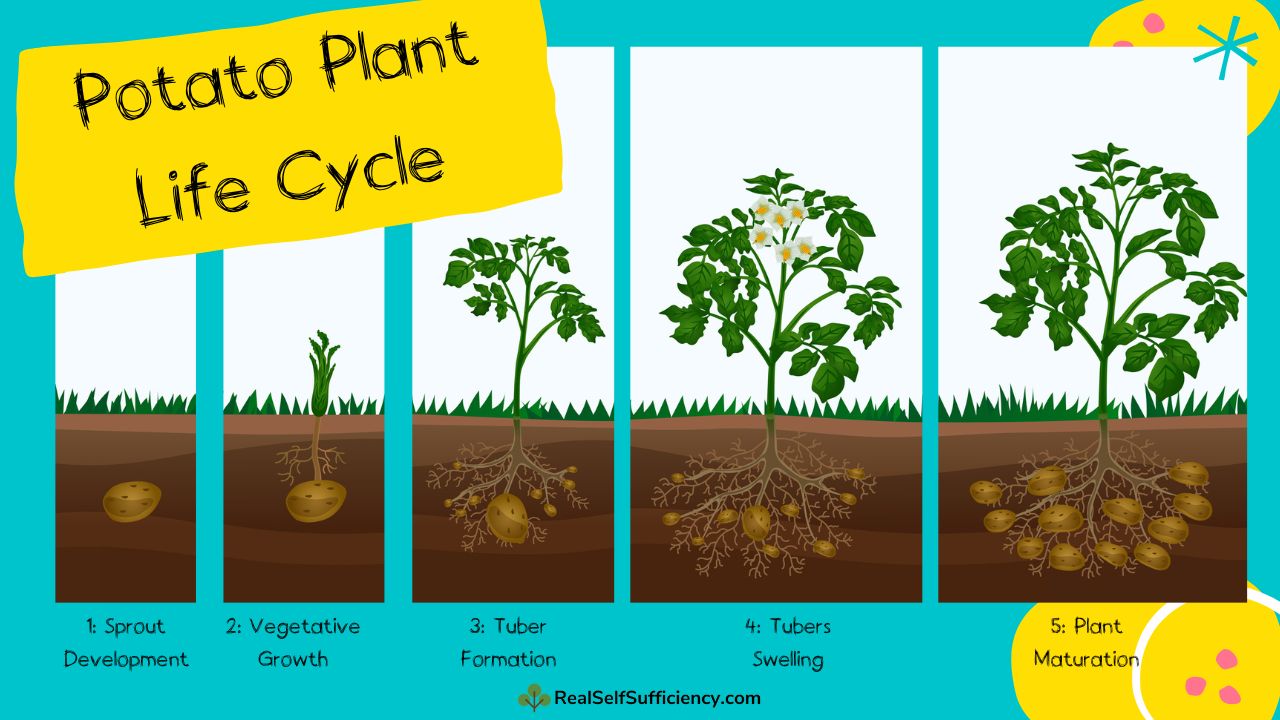
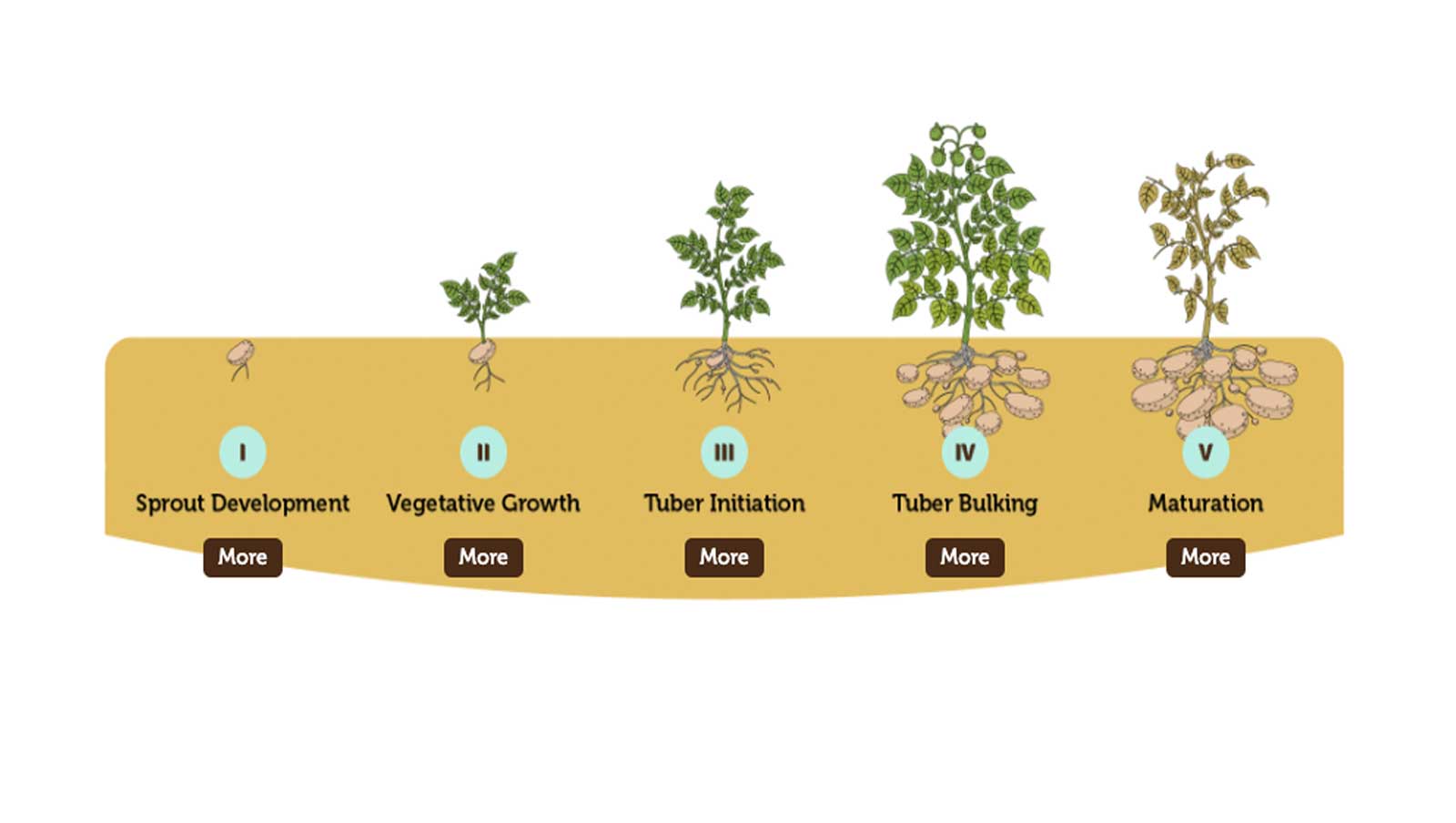
Growth Stages. Growth of a potato plant can be separated into five stages: sprout development, plant establishment, tuber initiation, tuber bulking, and maturation (Fig. 2.5). The transition from one stage to another is not always readily apparent. Timing of growth stages varies depending upon factors such as temperature.
19 Different Types of Potatoes
This is the very early stage of potato growth and small sprouts emerge from the soil, it sometimes takes more than a month to finish this stage. Growth Stage 2: (Vegetative Growth and Photosynthesis) Photosynthesis starts off evolving within the leaves and stems above the floor. Stolons (underground stems) broaden underground.
PPT Harvest Operations PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2461497
The growth of the potato plant continues to progress upward and outward until it eventually reaches the flowering stage, usually taking place around 8-9 weeks after planting. At this crucial phase, the plant redirects more of its energy toward the production of potatoes beneath the soil, therefore, its leaves and foliage will gradually start to reduce in height.

Potato Plant Growth Cycle Stock Illustration Download Image Now iStock
Note, of course, that this growth is rarely linear. In my experience, the bulk of top growth occurs early in the potato life cycle. Once it reaches a good size, the potato redirects its energy to tuber development and flowering. Growth Stages of Potato Plant. On average, potatoes need 90 to 120 days from planting to harvest.

Life cycle crop stages of potato Royalty Free Vector Image
Looking after the crop (Stages 2 & 3) Looking after the crop (Stage 4) Harvesting and marketing How to get ready for planting, prepare the seed and plant. THE CROP Growing 3 Things to do from planting to just before tuber initiation. 13 20 28 This section is our recipe for growing and marketing a commercial crop of potatoes for the fresh market.
PPT Potato Growth and Development Dr. Mike Thornton PowerPoint Presentation ID5678500
Vegetative Growth. The second stage of potato growth is the vegetative stage. The sprouts are now visible and the stems, leaves, and roots start developing. The important thing about this particular stage is that the plant starts performing photosynthesis to allow it to use light, water, and carbon dioxide for further development.

Potato Growth Stages and Growing Quick Tips Harvest to Table
The second stage of growth is the most difficult to predict, but it is the most important. During this time, the temperatures should be at least seventy-seven degrees Fahrenheit and fourteen to eighteen hours of sunlight. Stage 2: The Vegetative Stage. The vegetative stage is the beginning of the potato plant's growth cycle.

Potato Growing Stages Composition Stock Vector Illustration of garden, vegetarian 237937478
At this stage the seed tuber provides the nutrients necessary for growth but you'll need to keep the soil evenly moist for optimal growth. Stage 3 - Vegetative growth . The next stage of potato growth is the vegetative growth phase and this is when the leaves, roots and stolons appear. This is also the stage when photosynthesis begins.

Potatoes Plant Growing Process from Seed To Ripe Vegetables. Infographic of Potato Growth Stages
Potato plants have differing nutrient requirements at different growth stages. Growth Stage 1 The nutrient requirement is 100% dependent from the seed piece. Growth Stage 2 The nutrient requirement is still 25% dependent from the seed piece. The remaining nutrient requirement is quite small until row closure. Growth Stage 3 This stage takes 7.

Potato Crop Growth Stages
The final stages of potato growth are maturation and harvest. When the potato plant leaves turn yellow and die back, it's an indication that the potatoes are ready to be harvested. It typically takes around 2-4 weeks. Depending on the variety, the time from planting to harvest can range from 70 to 120 days.

Potato life cycle Greenhouse Today
Optimal Conditions for Stage 1. Potatoes sprout easily in acidic soil with pH values between 6 and 6.5 that's kept at temperatures above 45°F. Water them when the top 2 inches of soil feel dry. You may grow your potatoes in soil with pH levels as slow as 5.2. For best growth, however, plant them in slightly acidic soil-soils between 6 and.
Life Cycle of a Potato What You Need to Know
The tuber growth stage, also known as tuber bulking, is when your potato tubers grow larger. Between 45 and 90 days after the first sprouts emerge, the tubers produced during the tuber formation stage will grow from tiny buds to full-size potatoes.
Potato Development and Growth Staging
Stage 1: Early Stage Potato Growing Stages - Sprout Development. During the early stage potato growing stages, the seed potato or piece begins its transformation into a thriving plant. This stage is characterized by the emergence of sprouts from the seed potato, which will eventually grow into the above-ground portion of the potato plant.

Potato Growth Stages How Fast Do Potato Plants Grow?
Sprout development is the very first stage of potato plant growth. The seed potato has "eyes" on it, and from there the new sprouts emerge. This is known as chitting. While it's not technically necessary to chit before planting, you stand a better chance of getting the potatoes to grow instead of rot if you take the time to chit them.

Potato growth 種種種 Pinterest
1 INTRODUCTION. Descriptions of phenological stages have been developed in order to systematically compare plant growth and development. For potato (Solanum tuberosum L.), various phenological scales of plants derived from seed tubers have been developed (Anon, 1987; Griess, 1987, 1989).Jefferies and Lawson indicated that most developed potato scales were not representative of all the stages.

Infographic or infochart of potato growth stages Vector Image
Potatoes are a cool-season crop and should be planted in soil that is 45 to 55 degrees Fahrenheit. "During the growing stage, the optimal temperature for potatoes is 60 to 70 degrees Fahrenheit," says Spoonemore. "Potatoes are not well-suited to hot temperatures and produce the best yield in regions with cooler nights and mild daytime.