
Types of Business Entities Whats Up SWFL
Here are the steps you'll need to take in order to get open an LLC in North Carolina. Step 1: Name your North Carolina LLC. Step 2: Choose a Registered Agent. Step 3: File articles of organization. Step 4: Create an Operating Agreement. Step 5: Comply with NC's tax requirements.

Types of Business Entities Everything You Need to Know Tailor Brands
The IRS views any business registered in another country as foreign. For example, if you register an LLC in the state of Ohio, you're considered a domestic LLC, regardless of whether you trade in another state. If you were to register an LLC in the United Kingdom and do business in the U.S. but not register in a U.S. state, you're a foreign.

A Simple Guide to the Different Types of Business Entities in the USA
In this A-Z guide, we'll walk you through the step-by-step process of creating an LLC with Tailor Brands. Whether you're a first-time business owner or an experienced one, this guide will provide you with everything you need to know to form an LLC through our platform. From choosing a name to filing paperwork, we'll cover all the essential.
/business-entities-3193420_final-9806a9e0701a4f60b9e06d36e0e0338b.png)
What Is a Business Entity?
Your business structure affects how much you pay in taxes, your ability to raise money, the paperwork you need to file, and your personal liability. You'll need to choose a business structure before you register your business with the state. Most businesses will also need to get a tax ID number and file for the appropriate licenses and permits.

Different Types of Business Entities Fast Filing
Wyoming created the first U.S. LLC to address the needs of local entrepreneurs who weren't in a position to start a corporation but wanted limited liability protection while maintaining the simplified tax structure of a sole-proprietorship and partnership.. As the popularity of LLCs grew (there are over 2.5 million in the U.S. today), individual states came to realize the need for different.

Different Types of Business Entities YouTube
Most business owners will choose from the six most common options: sole proprietorship, general partnership, limited partnership, LLC, C corporation or S corporation. Below, we've explained each.

Types of Business Entities Pros, Cons, and How to Choose
4. Limited Liability Partnership (LLP): Best for Professional Businesses. 5. C-Corporation: Best for Outside Investment Opportunities. 6. S-Corporation: Best for Multiple Owners Seeking Board.

Types Of Businesses
The five main entity types. Almost every business falls into one of these categories: Business entity type. Summary. Sole proprietorship. One person owns and controls the business. The owner pays all taxes and debts personally. here's no corporate entity. They report profits and losses on Schedule C of their personal tax return.
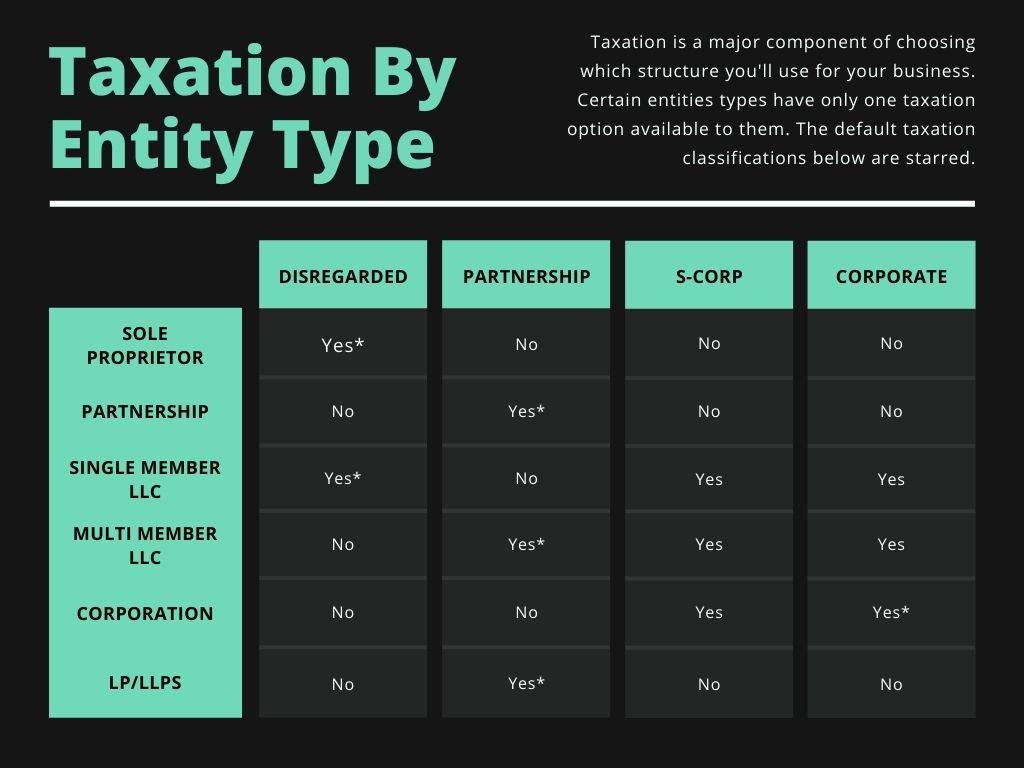
What Are The Different Business Entity Types? NC Business Blog
A business entity is the legal designation of an organization's structure. If you are planning to launch a venture or just want to start a side-hustle, picking the right business entity is critical. There are several different types of business entities: Sole Proprietorship Partnerships Corporations Limited Liability Company (LLC) The entity you pick can affect

7 Types of Business Entities (+ Pros and Cons) FounderJar
Sole Proprietorships. A sole proprietorship is an unincorporated business owned and operated by only one person. In terms of taxation and liability, the sole proprietor is the same as the sole.

Most Common Business Entities Joshua Wilson CPA
To make your bakery business a success, you need a mix of ingredients and this post is your recipe. The first ingredient is deciding on a bakery business model. 1. Retail. Retail bakeries sell their baked goods directly to the public, not other businesses, and there are several ways you can do it.

The 7 Most Popular Types of Business Structures Volusion
Unlimited personal liability. Financing difficulties. Many businesses start as a sole proprietorship. This is the most common type of business entity because it allows you to do business under your own name without going through the legal process of creating a separate entity.

Business Entity Types How To Select What’s Best For You Reality Paper
When 2+ people own a business together, they can form one of two types of partnerships: A limited partnership (LP) or a limited liability partnership (LLP). In an LP, one general partner has unlimited liability, while the other limited partners have limited liability. All partners pay personal income taxes on profits, but the general partner.
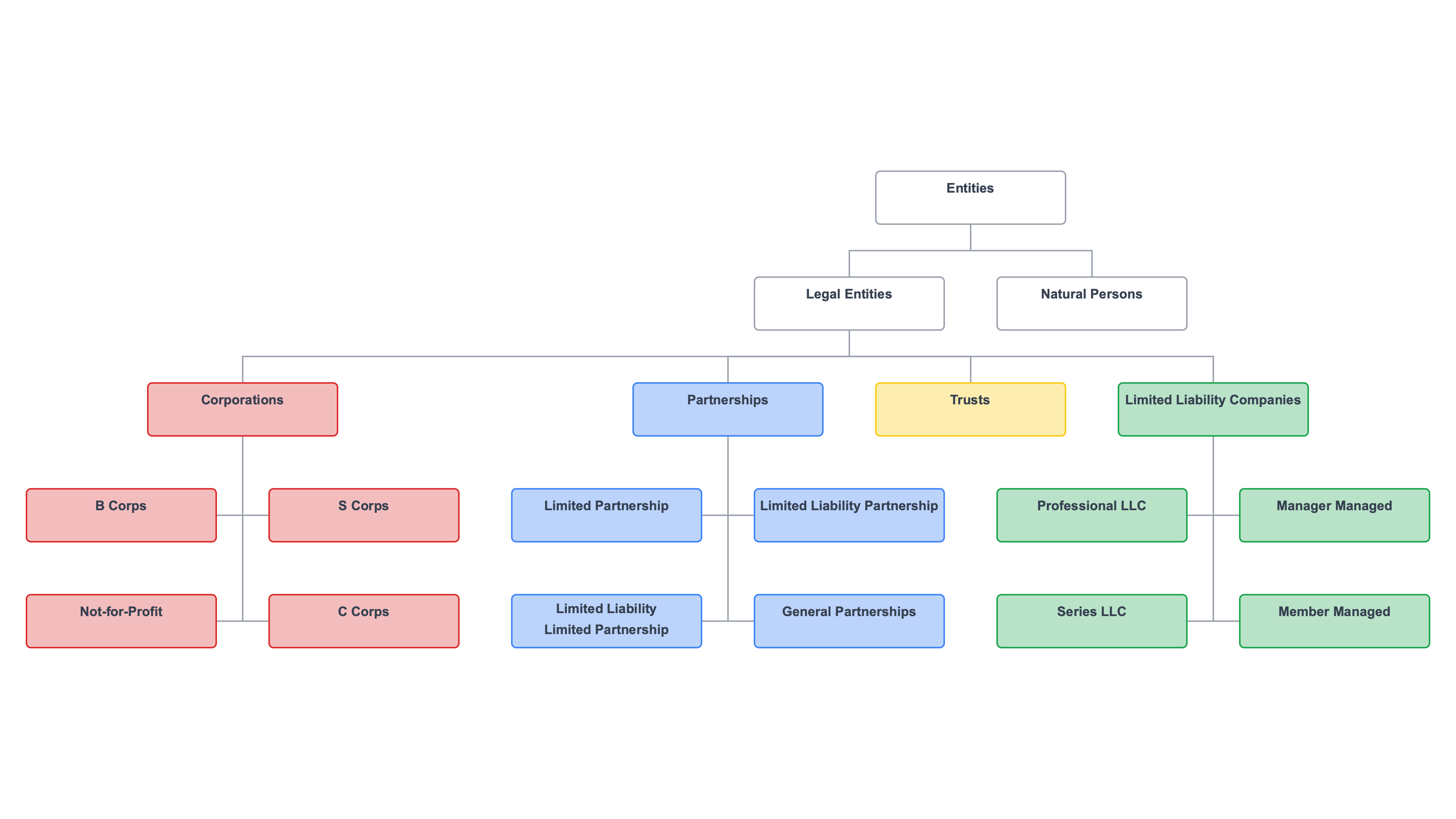
Hierarchy chart of business entity types
Different types of business entities have varying business structures and include LLC, limited liability partnership, partnership, sole proprietorship, corporation, and nonprofit. The type of corporation you choose depends on several factors. The following are the different types of business entities and what they each entail.

What are the types of Business entities? YouTube
Pros of general partnership. 1. Simplicity. Partnerships are an uncomplicated business to start, and they are relatively simple to run. 2. Partners control the business. A partnership allows the owners to run the company directly and allocate profits as they see fit. 3. Flexibility.

Business Entity Comparison Table Types of Business Entities
Corporation. A corporation is an authorized entity working under state regulation whose scope of business operations and identity are restricted by its articles of incorporation. Articles of incorporation should be filed with your state to become a corporation. If your business operations are in Delaware, for example, then you would file for a.